Concept explainers
Heat lamps are commonly used to maintain foods at about 50°C for as long as 12 hours in cafeteria serving lines. The following experiment was conducted to determine whether this practice poses a potential health hazard.
Beef cubes were surface-inoculated with 500,000 bacterial cells and incubated at 43–53°C to establish temperature limits for bacterial growth. The following results were obtained from heterotrophic plate counts performed on beef cubes at 6 and 12 hours after inoculation:
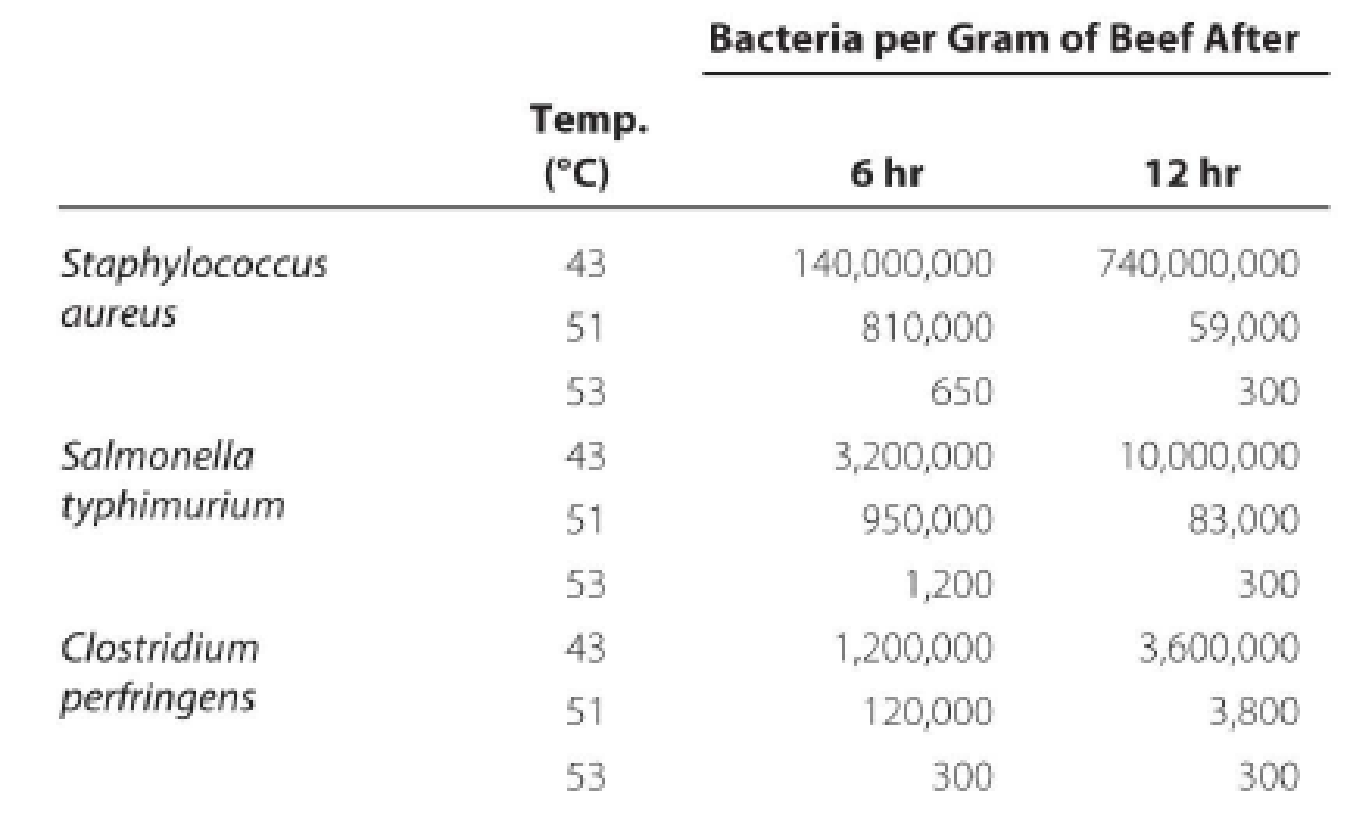
Draw the growth curves for each organism. What holding temperature would you recommend? Assuming that cooking kills bacteria in foods, how could these bacteria contaminate the cooked foods? What disease does each organism cause? (Hint: See Chapter 25.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (4th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (6th Edition) - standalone book
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
- Using your fingers, you are asked to aseptically touch the surface of a sterile agar plate. Illustrate the possible result from this step if your fingers are (a) unwashed – touched various things prior to placing on agar surface, and (b) washed with soap or disinfected with 70% alcohol. Describe the relative abundance of microbial growth observed on the plates. List and draw the possible characteristics of an isolated bacterial colony that can be observed based on type of (a) margin, (b) elevation, (c) texture, and (d) optical property.arrow_forwardTo determine the number of cells in a pure culture of Klebsiella pneumoniae, you have performed a serial dilution using three tubes of sterile saline (9.9 ml each). A sample of 0.1 ml from the culture was added to tube 1. Similarly, 0.1 ml from tube 1 was used to inoculate tube 2, and tube 3 was inoculated using 0.1 ml from tube 2. A nutrient agar plate was then inoculated using 0.1 ml from tube 3 and incubated overnight. The next day, 92 colonies were observed on the plate. How many cfu/ml were in the original culture? Using a Petroff-Hauser counting chamber, the number of cells in the same culture was estimated to be 8.5 • 109 cells/ml. How can you explain these results?arrow_forwardYou have found that the D-value (decimal reduction value) of an antimicrobial agent to be 4 minutes when the agent was exposed to a bacterial culture having an initial total viable cel1 count of 10° CFU/mL. After 4 minutes upon addition of the antimicrobial agent, what would have been the total viable count of the culture in this experiment? A) O 10° CFU/mL B) O 10$ CFU/mL C) O 10° CFU/mL D) O 10' CFU/mLarrow_forward
- Assume an inoculum with a cell density of 108 cells per mL. The entire generation time takes 30 minutes. How many hours would it take to grow a culture to 108/mL if you started with a 10–2 dilution? helpful formula: g (generation time) = 0.301 (time)/ log x – log xoarrow_forwardBacterial generation times for four different bacterial species were calculated in the media listed in Table 6.3. All media were prepared with pure distilled water and incubated aerobically in the light. Compare and contrast the growth requirements of the four bacteria listed above. Which of the media, if any, are chemically defined?| Generation Time Escherichia coli Pseudomonas Lactobacillus Nitrobacter Medium aeruginos a NaCl, NO3", MgSO4 80 Glucose 100 Glucose, NaCl, PO43- Glucose, NaCl, PO43-, MgSO4 Glucose, NaCl, PO4-, MgSO4, 56 200 43 100 28 40 8 amino acids Glucose, NaCl, PO43-, MgSO4, 25 25 80 19 amino addsarrow_forwardSydney Brenner isolated Salmonella typhimurium mutants that were implicated in the biosynthesis of tryptophan and would not grow on minimal medium. When these bacterial mutants were tested on minimal medium to which one of four compounds (indole glycerol phosphate, indole, anthranilic acid, and tryptophan) had been added, the growth responses shown in the following table were obtained. Mutant Minimal medium Anthranilic acid Indole glycerol phosphate Indole Tryptophan trp-1 − − − − + trp-2 − − + + + trp-3 − − − + + trp-4 − − + + + trp-6 − − − − + trp-7 − − − − + trp-8 − + − − + trp-9 − − − − + trp-10 − − − − + trp-11 − − − − + Give the order of indole glycerol phosphate, indole, anthranilic acid, and tryptophan in a biochemical pathway leading to the synthesis of tryptophan. Indicate which step in the pathway is affected by each of the mutations.arrow_forward
- How would you identify this unknown bacteria using a flowchart and the bacteria below as a possible unknown? Bacillus cereus, Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Lactococcus lactis. Create flow chart (dichotomues) using at least 3 other biochemical tests from the following list: Mannitol salt agar, Blood agar, Starch agar, Tributyrin Agar, Gelatin, Casein agar, Indole Production, MR-VP, Citrate, Hydrogen Sulfide test, Urease test, Nitrate reduction test, Catalase test, and Oxidase test.arrow_forwardThe following results were obtained from a disk diffusion test for microbial susceptibility to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus was the test organism. Use these data to answer questions. The following results were obtained using the Kirby-Bauer method to assess microbial susceptibility to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus was the experimental organism. Use the data below to answer the questions. antibiotics Zone of Inhibition TO 3mm В. 7mm C Omm 10mm The most effective antibiotic was: Select one: O TO B. can't tell O O O O Oarrow_forwardGiven the scenario, compute for the total volume of the culture media solution (milliliter or liter) and dehydrated media (grams). Scenario: The students of a Microbiology class were tasked to transfer or subculture a pure culture of Escherichia coli bacterium in five 7 mL nutrient broth and five petri dishes of nutrient agar with 20 mL capacity each. Based on the instruction bottles for nutrient broth and nutrient agar, preparation of the culture media is as follows. Nutrient broth: 8 g/liter Nutrient agar: 28 g/liter Formula: C1V1 = C2V2 *Concentration *Volume Computation: What are the answers to the following. Weight in grams of nutrient broth: _________ Distilled water in mL for nutrient broth: __________ Weight in grams of nutrient agar __________ Distilled water in mL for nutrient agar: ____________arrow_forward
- You are given a bacterial culture which has a concentration of approximately 5.0 x 10^8 cells/mL. List a series of dilutions and platings that you could carry out in order to determine the exact concentration of the culture. Note that you must plate four plates from a minimum of two dilution tubes. The volumes plated should be in the range of 0.1 mL – 1.0 mL. Duplicate volumes may not be plated from any one dilution tube. Each plating should aim for a count between 30 and 300 CFUs. You can select any value from 30-300 for CFU and any volume from 0.1-1.0 to find out dilution schemearrow_forwardWhat would you need to culture the following microorganisms? (Note the hints and/or choices after some blanks). Species A Species B Mesophile Thermophile Acidophile Neutrophile Obligate anaerobe Facultative anaerobe set to a (options: low (around 10 For Species A, you would need a(n) degrees C), mid-range (around 37 degrees C), high (around 65 degrees C), while for Species B, the temperature would need to be (options: low (around 10 degrees C), mid-range (around 37 degrees C), high (around 65 degrees C). (hint: nutrient source) that has a For Species A you would need a(n) (hint: the answer is a number). (options: low, high) pH, while for Species B, the pH should be around For Species A you should (choices: add, remove) oxygen. For Species B you should (choices: add, remove) oxygen. Earrow_forwardThe nutrient broth is a basic media used for growing a broad variety of microorganisms in the laboratory. The nutrient broth consists mainly of 1.5g * L ^ - 1 extract, 3g * L ^ - 1 yeast extract and 5g * L ^ - 1 sodium chloride dissolved in distilled water. The nutrient agar is prepared by adding the agar at the desired amount into nutrient broth. Answer the following questions. marks) a) How would you prepare a 500 ml nutrient broth? b) How would you prepare 2% (w / v) nutrient agar for 1L? c) How would you prepare a 100 ml nutrient broth supplemented with 100mu * g / m * l ampicillin antibiotic? The stock concentration for ampicillin solution is 100mg / m * l .arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





