
(a)
Interpretation:
A curved-arrow mechanism for the interconversion of
Concept introduction:
The interconversion of
Answer to Problem 25.35AP
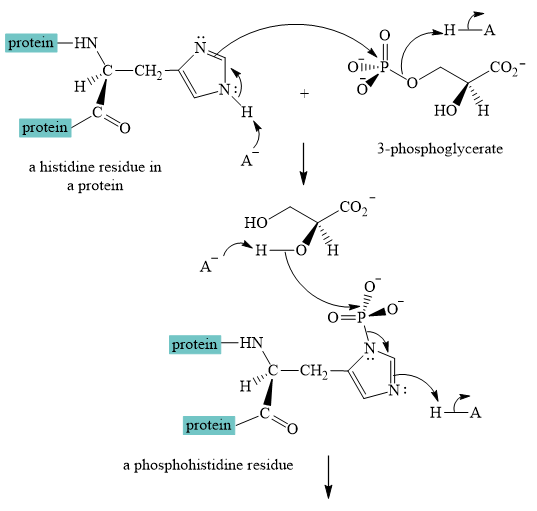
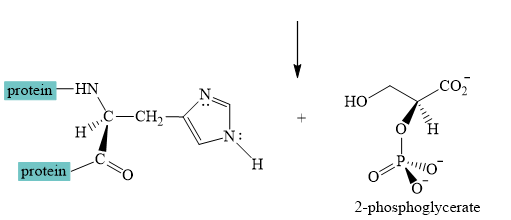
Explanation of Solution
The interconversion equation of
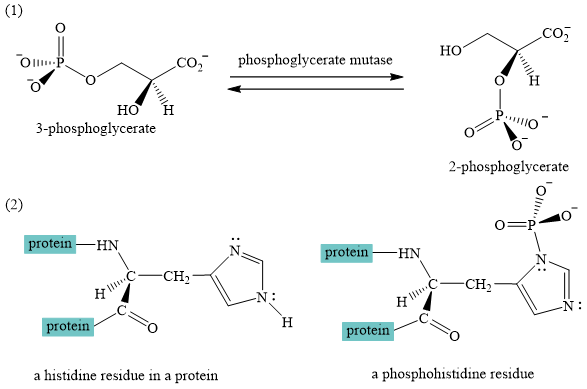
A curved-arrow mechanism for the interconversion of
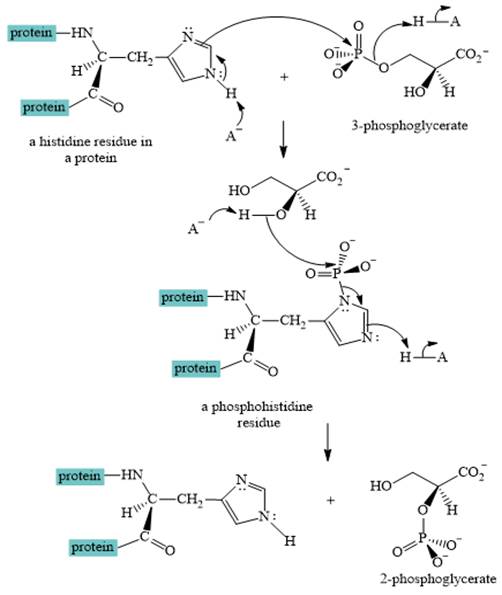
The nitrogen of histidine residue acts as a nucleophile after loss of proton by a base
The two step curved arrow mechanism for the interconversion of
(b)
Interpretation:
If the isotopically chiral
Concept introduction:
The enzyme catalyzed substitution reaction of phosphate ester derivate at phosphate proceeds through
Answer to Problem 25.35AP
If enantiomerically pure
Explanation of Solution
The enzyme catalyzed substitution reaction of phosphate ester derivate at phosphate proceeds through inversion of stereochemistry. The substitution occurs twice with double inversion of the product formed with retention of configuration. Thus, if enantiomerically pure
The interconversion of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the product (from the image below) of the starting material D-glyceraldehyde which will (1) produce aldaric acid upon reacting with HNO3 + H2O, NaOCH2, NH2OH, and (CH3CO)2O + NaOCOCH3 (2) produce tartaric acid upon reacting with HNO3 + H2O, NaOCH3, NH2OH, and (CH3CO)2O + NaOCOCH3arrow_forwardPredict the products formed when the following sugars react with excess acetic anhydrideand pyridine.(a) a-d-glucopyranose (b) b-d-ribofuranosearrow_forwardThe activity of an enzyme requires a glutamic acid to display its -COOH functional group in the protonated state. Suppose the pK, of the -COOH group is 4.07. (a) Will the enzyme be more active at pH 3.5 or 4.5? Explain. (b) What fraction of the enzymes will be active at pH = 4.07? Explain. (c) At what pH will the enzyme show 78% of maximal activity?arrow_forward
- Identify monomeric and multimeric (di-,tri-meric, for example) saccharides from this group. If you come across multimeric polypeptides, state the mono- mers that form these multimers. State the nature of the bond that links two units together in each case. (a) Maltose (b) Trehalose (c) Lactose (d) Sucrose (e) Cellobiose (f) Agarosearrow_forwardEsterase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters. It hydrolyzes esters of L-amino acids more rapidly than esters of d-amino acids. How can this enzyme be used to separate a racemic mixture of amino acids?arrow_forwardANSWER ALL QUESTIONS 4(a) Suggest a test you will use to show that a given food substance contains protein. Show how you will use Modified Gabriel’s Synthsis Streckers’s Synthesis to prepare phenylalanine in the laboratory. 5 (a) Describe in detail how you will determine the primary structure of protein. You have been given a mixture of lysine, histidine and cysteine. The isoelectric point of the amino acids are as follows: Histidine 7.64 Lysine 9.74 Cystenie 5.02 Show how you will separate the mixture into the pure forms. State and describe any instrument that you will use to separate the components in the mixture.arrow_forward
- 3a. 3b. 3c 3d. 3e. CO₂ clavulanic acid CH₂-OH H Answer the following questions about clavulanic acid. Does clavulanic acid inhibit D-alanyl-D-alanine transpeptidase? Does clavulanic acid contain a ß-lactam? Does clavulanic acid contain a thiazolium ring? What is the result of the treatment of penicillinase with clavulanic acid? Does clavulanic acid form a covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate with penicillinase?arrow_forwardAn optically active D-aldopentose (A) produced an optically inactive alditol (B) upon treatment with H2/Pt. When the aldopentose (A) was subjected to a Ruff degradation, D-aldotetrose (C) was generated. The aldotetrose (C) gave an optically active aldaric acid (D) upon oxidation with HNO3. D-aldopentose (A) can be prepared from D-threose by a Killani Fischer synthesis. Propose structure of A through D.arrow_forwardIs gentiobiose a reducing sugar? Does it mutarotate? Explain your reasoningarrow_forward
- Explain, using Le Châtelier’s principle, why the equilibriumconstant for the formation of NO from N2 and O2increases with increasing temperature, whereas the equilibriumconstant for the formation of NO2 from NO and O2decreases with increasing temperature.arrow_forwardCarbonic anhydrase facilitates the dissolution of carbon dioxide gas into water by catalyzing its hydration. Is the catalyzed reaction efficient? By what criterion do you state that?arrow_forwardThe amino acid (S)-alanine has the physical characteristics listed under the structure. What is the optical rotation of a racemic mixture of (R)- and (S)-alanine?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
