
Concept explainers
A circular bar ACB of a diameter d having a cylindrical hole of length .r and diameter till from A to C is held between rigid supports at A and B. A load P acts at U2from ends A and B. Assume E is constant.
(a) Obtain formulas for the reactions R, and RBat supports A and B. respectively, due to the load P (see figure part a).
(b) Obtain a formula for the displacement S at the point of load application (see figure part a).
(c) For what value of x is RB= (6/5)?,? (See figure part a.)
(d) Repeat part (a) if the bar is now rotated to a vertical position, load P is removed, and the bar is hanging under its own weight (assume mass density = p). (See figure part b.) Assume that
x = LI2.
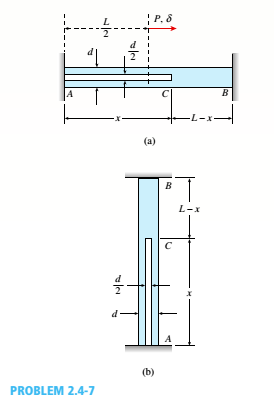
(a)
The formulas for the reactions at the point A and point B due to the load.
Answer to Problem 2.4.7P
The reaction force at point B is
The reaction force at point A is
The reaction force at point B is
The reaction force at point A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The Diameter of circular bar is
The figure below shows the free body diagram of the bar.
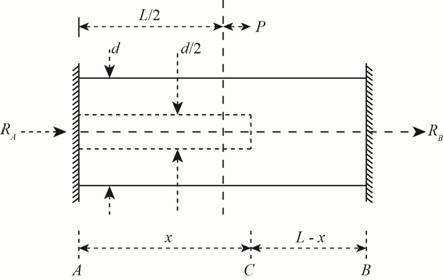
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the area when
Here, the area of the section AC is
Write the expression for the elongation of the bar at point B .
Here, load is
Write the expression for the area of bar CB when
Write the expression for the elongation at point B .
Write the expression for the elongation at point B in terms of the reaction force.
Here, the reaction force at point B is
Write the compatibility equation if
Write the expression for the rod held under rigid supports if
Write the expression for the force balance in horizontal direction.
Here, the reaction force at point A is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reaction force at point B is
The reaction force at point A is
The reaction force at point B is
The reaction force at point A is
(b)
The formula for the displacement at the point of load.
Answer to Problem 2.4.7P
The displacement at the point of load is
The displacement at the point of load is
The displacement at the point of load is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the displacement at the point of load if
Here, the reaction force at point A is
Write the expression for the load at point if
Here, the reaction force at point A is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The displacement at the point of load is
The displacement at the point of load is
The displacement at the point of load is
(c)
The value of
Answer to Problem 2.4.7P
The value of
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the reaction force at B if
Write the expression for the reaction force at B case if
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The value of
The value of
(d)
The formulas for the reactions at the point A and point B due to the load.
Answer to Problem 2.4.7P
The reaction force at point B is
The reaction force at point A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The bar is placed vertically.
The below figure shows the free body diagram of the bar.
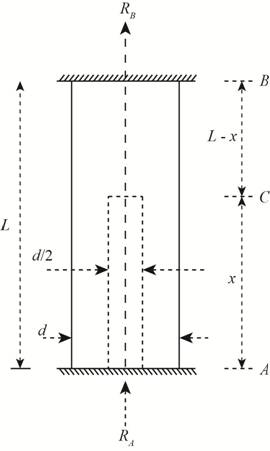
Figure-(2)
Write the compatibility equation if 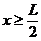
Write the expression for the elongation at point B in terms of the reaction force.
Write the expression for the elongation of the bar at point B .
Here, the axial stress in section AC is
Write the expression for the axial stress in section AC is
Here, the density is
Write the expression for the axial stress in section CB is
Write the expression for the elongation of the bar held between rigid bars.
Write the expression for the reaction at point A .
Here, the weight of the bar of section AC is
Write the expression for the weight of the bar of section AC .
Write the expression for the weight of the bar of section CB .
Substitute
Calculation:
Substitute 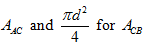 in Equation (XVII).
in Equation (XVII).
Substitute 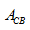 in Equation (XIX).
in Equation (XIX).
Substitute 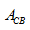 in Equation (XX).
in Equation (XX).
Substitute, 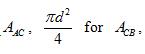
Integrate the Equation (XXIV).
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute 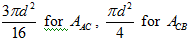 in Equation ......(XXV).
in Equation ......(XXV).
Conclusion:
The reaction force at point B is
The reaction force at point A is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





