
A couple M with a magnitude of 100 N·m is applied as shown to the crank of the engine system. Knowing that AB = 50 mm and BC = 200 mm, determine the force P required to maintain the equilibrium of the system when (a) θ = 60°, (b) θ = 120°.
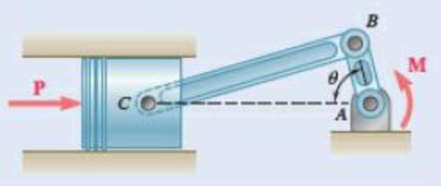
Fig. P10.22
(a)
Find the magnitude of the force P required to maintain the equilibrium.
Answer to Problem 10.22P
The magnitude of the force P required is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The magnitude of the couple M is
The distance between the point A and B is 50 mm.
The distance between the point B and C is 200 mm.
The value of the angle
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the engine system as in Figure 1.
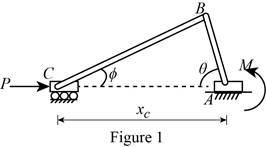
Consider the geometry of the Figure 1.
Use the Law of sines;
Differentiate the equation;
Find the horizontal displacement
Differentiate the equation;
Substitute
Use the principle of virtual work;
Substitute
Substitute 50 mm for AB, 200 mm for BC, and
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of the force P required is
(b)
Find the magnitude of the force P required to maintain the equilibrium.
Answer to Problem 10.22P
The magnitude of the force P required is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The magnitude of the couple M is
The distance between the point A and B is 50 mm.
The distance between the point B and C is 200 mm.
The value of the angle
Calculation:
Refer part (a) for calculation;
Substitute 50 mm for AB, 200 mm for BC, and
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of the force P required is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- A 4-kN force P is applied as shown to the piston of the engine system. Knowing that AB = 50 mm and BC = 200 mm, determine the couple M required to maintain the equilibrium of the system when (a) θ= 30°, (b) θ= 150°.arrow_forwardFor the shown frame and loads P=756 KN and Q=1512 KN, - 3 m 1.5 m 1 m 8 m 6 m magnitude of y-component of reaction at B (KN) a. 168 b. 210 C. 252 d. 262.5 e. 294 magnitude of x-component of reaction at B (KN) a. 6552 b. 4368 с. 5460 d. 2184 e. 7644 magnitude of x-component of reaction at C (KN) magnitude of y-component of reaction at C (KN) magnitude of y-component of reaction at A (KN)arrow_forwardTwo rods AC and CE are connected by a pin at C and by a spring AE . The constant of the spring is k , and the spring is unstretched when θ = 30°. For the loading shown, derive an equation in P,θ ,I, and k that must be satisfied when the system is in equilibrium.arrow_forward
- 9. A man is trying to pull the sled by applying a force of 500 N, as shown. The weight of the stone and the sled is 800 N while the sled is about to slide (i.e., it is still in equilibrium). Determine the magnitude of the reaction force R. a. b. W = 800 N 650 N 700 N 0 R P = 500 N 30⁰ Cc. d. 750 N 800 Narrow_forwardDenoting the coefficient of static friction between collar C and the vertical rod by μs , derive an expression for the magnitude of the largest couple M for which equilibrium is maintained in the position shown, when θ=35°, I= 600 mm, and P = 300 N.arrow_forwardThe drive belt on a vintage sander transmits ½ hp to a pulley that has a diameter of d = 4 in. Knowing that the pulley rotates at 1450 rpm, determine the tension difference T1-T2 between the tight and slack sides of the belt.arrow_forward
- The pin at C is attached to member BCD and can slide along a slot cut in the fixed plate shown. Neglecting the effect of friction, derive an expression for the magnitude of the couple M required to maintain equilibrium when the force P that acts at D is directed (a) as shown, (b) vertically downward, (c) horizontally to the right.Fig. P10.18arrow_forwardDetermine the value of θ corresponding to the equilibrium position of the rod of Prob. 10.10 when I= 30 in., a= 5 in., P = 25 lb, and Q= 40 lb.Reference to Problem 10.10:The slender rod AB is attached to a collar A and rests on a small wheel at C . Neglecting the radius of the wheel and the effect of friction, derive an expression for the magnitude of the force Q required to maintain the equilibrium of the rod.arrow_forwardTwo rods are connected by a slider block as shown. Given: MB= 250 lb-in. MA MB 25° 15 in. A |B 15 in.- Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the couple MA required to hold the system in equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Eight identical 500 × 750-mm rectangular plates, each of mass m = 40 kg, are held in a vertical plane as shown. All connections consist of frictionless pins, rollers, or short links. In each case, determine whether (a) the plate is completely, partially, or improperly constrained, (b) the reactions are statically determinate or indeterminate, (c) the equilibrium of the plate is maintained in the position shown. Also, wherever possible, compute the reactions.arrow_forwardDetermine the value of θ corresponding to the equilibrium position of the rod of Prob. 10.12 when P = 80 N, and Q= 100 N.Reference to Problem 10.12:Knowing that the line of action of the force Q passes through point C , derive an expression for the magnitude of Q required to maintain equilibrium.arrow_forwardThe uniform 10 kg rod AB is supported by a ball and socket joint at A and by the cord CG that is attached to the midpoint G of the rod. Knowing that the rod leans against a frictionless vertical wall at B and that the tension in the cord CG, TCG=52.1 N, determine the following, Which of the following best approximates the moment of the weight of the structure about A? Choices: (7.36i + 29.4k) N-m(7.36i + 29.4j) N-m(29.4i + 7.36k) N-m(29.4i + 7.36j) N-marrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





