
Concept explainers
A thin-walled cylindrical container of diameter
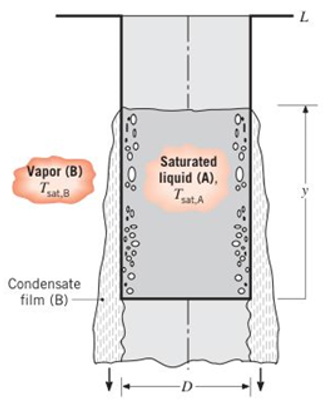
(a) For the portion of the wall covered with the condensate film, derive an equation for the average temperature of the container wall,
(b) At what rate is heat supplied to liquid-A?
(c) Assuming the container is initially filled completely with liquid, that is,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Applied Fluid Mechanics (7th Edition)
- Question 3 This question requires the use of the steam property tables (Rogers and Mayhew) uploaded on QM+ exam section. All properties should be evaluated at the temperature of the steam. Saturated, pure steam at a temperature of 170 °C condenses on the outer surface of a vertical tube of outer diameter 2 cm and length 1.5 m. The tube surface is maintained at a uniform temperature of 150 °C. Calculate: a) the local film condensation heat-transfer coefficient at the bottom of the tube. b) the average condensation heat-transfer coefficient over the entire length of the tube. c) the total condensation rate at the tube surface.arrow_forwardSaturated, pure steam at a temperature of 170 oC condenses on the outer surface of avertical tube of outer diameter 2 cm and length 1.5 m. The tube surface is maintained at auniform temperature of 150 oC.Calculate:a) the local film condensation heat-transfer coefficient at the bottom of the tube. b) the average condensation heat-transfer coefficient over the entire length of the tube. c) the total condensation rate at the tube surface.arrow_forward5 (a) (i) State two ways in which evaporation is different from boiling. (ii) Give one example of a change of state which does not invalve boiling orevaporation. (b) The graph in Fig. 5.1 shows the variation of temperature with time for a substance that is initially liquid. temperature Eime Fig. 5.1 O State what is taking place at points A, B and C. You should say what changes of state, if any, are taking place. point A point B point C (0 Suggest why the graph is steeper at point C than at point A.arrow_forward
- Estimate the power required to boil the water in a copper pan (Cs,f = 0.013 and n = 1), 180 mm in diameter. The bottom of the pan is maintained at 115 ℃ by the heating element of an electric range. Properties of Water (1 atm): Tsat = 100℃, ρl = 957.9 kg/m3, ρv = 0.5955 kg/m3, Cpl = 4217 J/kg.K, μl = 279*10^-6 N.s/m2, Prl = 1.76, hfg = 2257 kJ/kg, σ = 58.9*10^-3 N/m. Select one: a. 16420 W b. 18166 W c. 16240 W d. 11760 Warrow_forwardDiscuss the technical points on pressure- temperature diagram for condensate gas reservoir and explain This images about digram.arrow_forwardDiscuss the technical points on pressure- temperature diagram for condensate gas reservoir and explainarrow_forward
- Question 3 Which statement about vaporization enthalpy and condensation enthalpy is correct? O The condensation enthalpy is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign when compared to the vaporization enthalpy O There is no general relationship between these two quantities and the values depend on the substance involved. O The vaporization enthalpy is always less than the condensation enthalpy. O The vaporization enthalpy is exactly equal to the condensation enthalpy.arrow_forwardA steam trap is a device to purge steam condensate from a system without venting uncondensed steam. In one of the crudest trap types, the condensate collects and raises a float attached to a drain plug. Whenthe float reaches a certain level, it “pulls the plug,” opening the drain valve and allowing the liquid to discharge. The float then drops down to its original position and the valve closes, preventing uncondensed steam from escaping.(a) Suppose saturated steam at 25 bar is used to heat 100 kg/min of an oil from 135°C to 185°C. Heat must be transferred to the oil at a rate of 1:00 x 10 4 kJ/min to accomplish this task. The steam condenses on the exterior of a bundle of tubes through which the oil is flowing. Condensate collectsin the bottom of the exchanger and exits through a steam trap set to discharge when 1200 g of liquid is collected. How often does the trap discharge?(b) Especially when periodic maintenance checks are not performed, steam traps often fail to close completely…arrow_forwardB/A boiling channel receives a thermal power of 6000 kw. If subcooled water at 275 °C enters the channel at a flow rate of 15 kg/s what is the void fraction at the channel outlet where the slip ratio is 1.687 and pressure is 68 bar. Given data: At 68 bar: h=1256 KJ/Kg, hg-1518 KJ/Kg, V-1.344*10-³ m³/Kg, V-28.27*10³ m³/Kgarrow_forward
- Analyze the condensation process using both chillers. Provide operating temperatures and pressures entering each component shown in the diagram (at points 1, 2, 3, 4). Indicate which chiller should be chosen based on the economicsarrow_forwardUse the Kedzierski (2003) refrigerant/lubricant mixture pool boiling model to predict the boiling heat transfer coefficient (hm) for a range of superheats (4T, = 8 K to 40 K) and Ts = 277.6 K: 5.9×107(1−x,)ph ATk, (1-e*) x, To Where 1₂ %₁ = = 9m T-T Г x Τσ PL-Pbx 5.9×107(1-x₂)ph AT 0.755lp₁ (1-x₁) _ 18.75õ₁ (1—x₁) _ 18.75×10¯¹º[m]p, (1-x₂) Xp Prv XpPrv XpPrv Assume that λ = 1.34 for xb=0.005 and that λ = 0.3 for Xb = 0.02. The properties of the refrigerant (R123) at the film temperature are: KL (W/mK) 0.139 R123 Or (N/m) 179692.3 0.01764 hfg (J/kg) The properties of the mineral oil (lubricant) are: PL (kg/m³) 917.8 York-C VL (cSt) 60 Prv (kg/m³) 2.701 VL (m²/s) 6 × 10-5 OL (N/m) 0.026 1.) Plot hm vs ATs and le vs ATs for two lubricant mass fractions: x = 0.005 (use 2 = 1.34 for Xb = = 0.005) and x = 0.02 (use λ = 0.3 for xb = 0.02). Compare the predicted ro for the two mass fraction cases. Provide a plausible reason for why the boiling heat transfer coefficient for a given AT's for…arrow_forwardOnly answer if you are 100% sure otherwise i will downvote... An ASTM B75 copper tube sheathes a heating element that is used to boil water at 1254 kPa. The copper tube is immersed horizontally in the water, and its surface is polished. The tube diameter and length are 5 mm and 9.5 cm, respectively. The maximum use temperature for ASTM B75 copper tube is 204°C. Determine the highest evaporation rate of water that can be achieved by the heater without heating the tube surface above the maximum use temperature. Use the property tables to calculate the properties of water at saturation temperature. The surface tension 0 at 190°C is 0.03995 N/m. Also, Csf 0.0130 and 10 for the boiling water on a polished copper surface. The highest evaporation rate of water is g/s?arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
