
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Out of the two distances between two nitrogen atoms, 50 pm or 75 pm, it is to be determined which one represents higher energy.
Concept introduction:
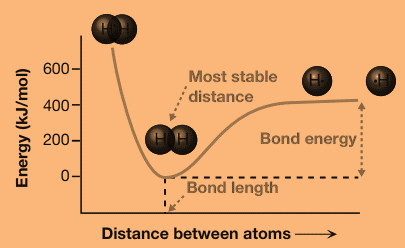
The energy of the molecule depends on the distance between the two atoms. At a certain distance, called the bond length, the energy reaches a minimum. As the distance between the two atoms increases, the energy of the molecule increases and slowly approaches a constant value as the distance increases to infinity. At distances shorter than the bond length, the energy increases very rapidly.
(b)
Interpretation:
Out of the two distances between two nitrogen atoms, 75 pm or 110 pm, it is to be determined which one represents higher energy.
Concept introduction:
The energy of the molecule depends on the distance between the two atoms. At a certain distance, called the bond length, the energy reaches a minimum. As the distance between the two atoms increases, the energy of the molecule increases and slowly approaches a constant value as the distance increases to infinity. At distances shorter than the bond length, the energy increases very rapidly.

(c)
Interpretation:
Out of the two distances between two nitrogen atoms, 110 pm or 150 pm, it is to be determined which one represents higher energy.
Concept introduction:
The energy of the molecule depends on the distance between the two atoms. At a certain distance, called the bond length, the energy reaches a minimum. As the distance between the two atoms increases, the energy of the molecule increases and slowly approaches a constant value as the distance increases to infinity. At distances shorter than the bond length, the energy increases very rapidly.

(d)
Interpretation:
Out of the two distances between two nitrogen atoms, 150 pm or 160 pm, it is to be determined which one represents higher energy.
Concept introduction:
The energy of the molecule depends on the distance between the two atoms. At a certain distance, called the bond length, the energy reaches a minimum. As the distance between the two atoms increases, the energy of the molecule increases and slowly approaches a constant value as the distance increases to infinity. At distances shorter than the bond length, the energy increases very rapidly.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- | and the US. what is the hy bri zation or the central atom inclo-?arrow_forward(a) What are valence electrons? (b) How many valence electrons does a nitrogen possess? (c) An atom has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p2. How many valence electrons does the atom have?arrow_forwardQ1. This question is about atomic structure. (a) Write the full electron configuration for each of the following species. CH Fe2+ (b) Write an equation, including state symbols, to represent the process that occurs when the third ionisation energy of manganese is measured. (c) State which of the elements magnesium and aluminium has the lower first ionisation energy Explain your answer. (d) A sample of nickel was analysed in a time of flight (TOF) mass spectrometer. The sample was ionised by electron impact ionisation. The spectrum produced showed three peaks with abundances as set out in the table. m/z Abundance /% 58 61.0 60 29.1 61 9.9 Give the symbol, including mass number, of the ion that would reach the detector first in the sample. Calculate the relative atomic mass of the nickel in the sample. Give your answer to one decimal place. Page 2 of 12 Symbol of ion Relative atomic massarrow_forward
- Na +, K +, Ca 2 +, and Mg 2 + are the four major cations in the body. For each cation, give the following information: (a) the number of protons; (b) the number of electrons; (c) the noble gas that has the same electronic confi guration; (d) its role in the body.arrow_forwardD ОН -ОН H30 (trace) H2O ? НО HN но -ОН HN. LOHarrow_forwardWhat is the electron configuration of Al 3* ? O (Ne) 4s2 3p! O (Nc|4s? O (Ar) O (Nc] O (Nc) 25? 3p!arrow_forward
- Consider the setup below. 20cm 10cm 1µC -1µC 1µC 1. Which direction will the negative charge in the center be pushed. [Choose one]. (a) The middle charge will experience a force to the left. (b) The middle charge will experience a force to the right. (c) The middle charge won't experience a force either way.arrow_forwardQ25. Identify the following atoms or ions from their electron configurations: (a) W: 1s 2 2s 2 2p6 3s 2 3p6 4s 2 3d10 4p6,5s1 (b) X-: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 (c) Y++: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s 2 3p6 4s 2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 (d) Z: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f 11arrow_forwardPauli exclusion principle specifies that each (1) can hold (2) two electrons, which must have (3) spins. (1) = electron state, (2) = more than, (3) = opposite. (1) = subshell, (2) = more than, (3) = the same. (1) = electron state, (2) = no more than, (3) = opposite. (1) = subshell, (2) = no more than, (3) = opposite.arrow_forward
- 5.) Electron Configurations for Ions: Supply the ground state electron configurations for the following ions. You many use the short-hand notation (e.g. Na*: [He]2s 2p°). (a) N (b) Mg*. (c) O (d) Sc* (e) Sn2+ (f) Ar 6.) Formulas of Ions: Predict the formulas of the most stable ions of the following elements (a) Na (b) Mg (c) S (d) Al (e) Br (f) Parrow_forwardIn a 1911 paper, Ernest Rutherford said: In order to form some idea of the forces required to deflect an alpha particle through a large angle, consider an atom containing a point positive charge Ze at its center and surrounded by a distribution of negative electricity, – Ze uniformly distributed within a sphere of radius R. Derive an expression for the magnitude of the electric field at the center of the atom. - Express your answer using the parameters +Ze and -Ze.arrow_forwardGroup the electronic configurations of neutral elements in sets according to those you would expect to show similar chemical properties. 15²2s²2p²38²3p³ 1s²2s²2p³: Set A 1s²2s²2p 3s²3p: 15²25²2p% 15² 3400 4p/5 1s²2s22p 3s23p648²3d¹04p6: 1s²2s²2p638²3p³: Answer Bank Determine the chemical symbols for the neutral elements corresponding to the electronic configurations. Use proper formatting; letter case matters. 1s²2s²2p³ 35²3p² 13²23²2p³ Set Barrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning

