
Set up the circuit with two bulbs in parallel as shown.
Rank the currents through bulb 1, bulb 2, and the bulb n the single bulb circuit from part A. Explain.
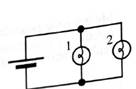
How does the current through bulb 1 compare to the current through the battery? Explain.
Measure the potential difference across each circuit clement
1. How does the potential difference across the battery in this circuit compare to the potential difference across the battery in the single-bulb circuit?
2. Rank the potential difference across bulb 1, bulb 2, and the bulb in the single-bub circuit from part A.
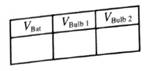
3. How does the ranking by potential difference compare to the ranking by brightness?
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 6 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Physics: Principles with Applications
College Physics
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
- Problem solving. Show your solutions every question. 1. A battery is connected across a light bulb with an internal resistance of 80 ohms. Using an ammeter, the current flowing in the circuit was measured to be 150 mA. What is the voltage of the battery? 2. A hair dryer pulls a current of 8000 mA from a 120 V power source. What is the internal resistance of the hair dryer? 3. What is the value of voltage in the picture?arrow_forwardRank the current through all the bulbs for each of the following circuits. Explain your reasoning. For circuit 4, draw an ammeter that will measure the current through the bul at the bottom left. Explain your reasoning. 1 1 3.arrow_forwardDirections: Solve for the given problems. Show your complete solutions. Round off your answers into 3 significant figures. 3. An ideal voltmeter is connected to a 2.0-Ω resistor and battery with emf of 5.0 V and an internal resistance of 0.5 Ω as shown in figure 6. a. What is the current in the 2.0-Ω resistor? b. What is the terminal voltage of the battery? c. What is the reading on the voltmeter?arrow_forward
- Solve for the given problems. Show your complete solutions. Round off your answers into 3 significant figures Refer to figure 7. a. Find the current in the circuit. b. Find the terminal voltage Vab of the 16.0-V battery. c. Compute for the potential difference Vac.arrow_forwardSimply the circuit to get the equivalent circuit. Show all circuits step by step. R1= 8 ohms, R2= 30 ohms, R3= 6 ohms, R4= 9 ohms, V= 54V A. What is the equivalent resistance?B. What is the current in R2?C. What is the potential difference across R3?D. What is the power dissipated in R4?arrow_forwardBuild the circuit shown with three resistors, four ammeters and a battery. Determine the values of current (amps) and electric pressure (volts) at the indicated locations. 2. How does the current in each resistor (11, 12, 13) compare to one another and to the current in the battery (In)? 3. How does the electric potential difference across the battery (AVB) compare to the summative electric potential differences of the three resistors (AV₁ +AV₂ + AV₁)? 4. Write the above relationship as an equation: 5. Calculate the ratio of electric potential difference to current for the battery. How does this ratio compare to the resistance values of the resistor? Attempt to write an equation relating the AVB/Is ratio to R₁, R₂, and R, values?arrow_forward
- How will the brightness of bulbs A and B change if bulb C is unscrewed? Will the result be different if bulb D or E is unscrewed instead? Explain. 7. Consider the circuit shown on the right. Are the bulbs C, D, and E connected in series, parallel, or neither? Explain. Parallel b/c the junction point is above point D where the current spreads a. Rank the bulbs in order of bright- ness. Use the symbols =, . Explain your ranking. b. с.arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions and show your work. 1. Consider the following set of light bulbs. Assume that all the light bulbs are identical. (all R €84 a. Which group of light bulbs emits more light? b. If the light bulb in group 2 suddenly burns out, what happens to the light bulbs in group 1? c. What happens to the circuit seen if the circuit is broken between the two light bulbs in group 1? 2. Determine the equivalent resistance between A and B the figure below. FREZZLESSand R=30 www wwwwww R-40 3. Consider the circuit drawn below. Find the values of each of the currents. R=40 L R=10 Son 380 J00 8 الشان 4047044S Parrow_forwardAt right is a basic circuit model of real batteries. Explain how the internal resistance affects the voltage the (real) battery can supply. Explain how it affects the energy one can extract from the battery.arrow_forward
- 9 V B. The circuit at right is made from an ideal battery connected to 4 ideal resistors as shown. i. What is the total resistance of this circuit? Show your work. R4= 352 R1 = 152 R3 = 452 ii. Find the current through each of the 4 resistors. Show your work. R2= 752 iii. Rank the potential difference across the 4 resistors from greatest to least. Explain your reasoning. iv. If resistor R3 is cut out of the circuit, without replacing it with anything, will the current through resistor R2 increase, decrease, or stay the same? Explain your answer or show your work.arrow_forwardConsider the diagram at the right of a series circuit. Each light bulb in the circuit has an identical resistance. Use the labeled points on the diagram to answer the following questions. Each question may have one, less than one, or more than one answer. a. The electric potential at point A is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. b. The electric potential at point C is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. c. The electric potential at point F is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. d. The electric potential at point I is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. e. The electric potential difference between points A and B is the same as the electric potential difference between points ___ and ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. f. The electric potential difference between…arrow_forwardDirections: Write the letter of your answer on a separate sheet of paper.1. With 21 V applied, if R1 = 5 ohms, R2 = 35 ohms, and R3 = 14 ohms, whatis the current in R2 if R1 is connected in series with the parallel circuit R2and R3?A. 200 mA B. 400 mA C.600 mA D.800 mA 2. What is the total resistance of a circuit when R1 (7 kΩ) is in series with aparallel combination of R2 (20 kΩ), R3 (36 kΩ), and R4 (45 kΩ)?A.4 kΩ B.17 kΩ C. 41 kΩ D. 108 kΩarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





