
Concept explainers
(a)
The time taken by the rock thrown from the edge of a cliff to reach the ground.
(a)
Answer to Problem 50P
The rock takes 2.93 s to reach the ground.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The depth of the ground from the top of the cliff,
Velocity of projection
,
Angle of projection,
Formula used:
The time taken to reach the ground is determined using the expression
Here,
Calculation:
The path of the rock is shown in the diagram below:
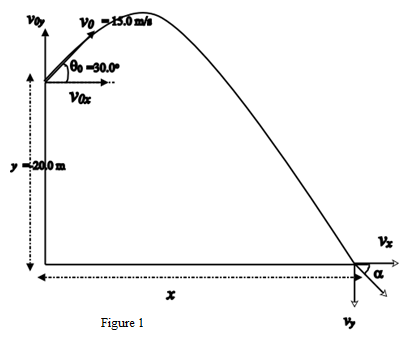
Calculate the value of
Substitute the values of variables in equation (1).
Rewrite the equation as follows:
Solve the quadratic equation.
Take the positive root, since time cannot have a negative value.
Conclusion:
Thus, the rock takes 2.93 s to reach the ground.
(b)
The horizontal distance between the point of projection and the point where the rock lands on the ground.
(b)
Answer to Problem 50P
The rock lands at a horizontal distance of 38.1 m from the point of projection.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Velocity of projection,
Angle of projection,
Time of flight of the rock,
Formula used:
The horizontal component of the rock’s velocity is constant, since no force acts on the rock in the horizontal direction in the absence of air resistance.
The horizontal distance travelled by the rock in a time t is given by,
Here, the horizontal component
Calculation:
Substitute the given values in equation (4) and calculate the value of
Substitute the values of
Conclusion:
Thus, the rock lands at a horizontal distance of 38.1 m from the point of projection.
(c)
The velocity of the rock when it lands on the ground.
(c)
Answer to Problem 50P
The velocity of the rock when it lands on the ground is found to have a magnitude
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The horizontal component of the rock’s initial velocity,
The vertical component of the rock’s initial velocity,
Time of flight of the rock,
Formula used:
The vertical component of the rock’s velocity when it reaches the ground is given by the expression,
The horizontal component of the rock’s velocity when it reaches the ground remains unchanged during its motion. Therefore,
The magnitude of the velocity of the particle when it reaches the ground is given by,
The angle made by the velocity vector to the horizontal is given by the expression,
Calculation:
Calculate the vertical component of the rock’s velocity when it reaches the ground by substituting the values of the variables in equation (5).
Since
Substitute the values of
Substitute the values of
Conclusion:
Thus the velocity of the rock when it lands on the ground is found to have a magnitude
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics Fundamentals
- Jack Sparrow stands on top of a cliff 82.0m tall and throws a rock with an initial velocity of 28.0m/s at an angle of 15.0° below the horizontal. a) How far from the base of the cliff will rock land? b) What will be the velocity of the rock when it reaches the ground?arrow_forwardA LASS swim team member is practicing her diving. She takes off with a velocity of 6.00 m/s [ 40° above the horizontal] from a diving board which is 5.00 m above the water surface. a) How long is she in the air? b) How far from the edge of the diving board will she land? c) What is her final velocity as she hits the water?arrow_forwardA cannonball is fired off a cliff at an angle of 25 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The cliff is 80 m high. The initial speed of the rock is 50 m/s. (a) What is the range of the rock? (b) When the cannonball hits the ground what is the magnitude of its total velocity?arrow_forward
- An object is thrown off of a cliff 320 m above level ground with an initial horizontal velocity of 20 m/s. How far from the building did the rock land?arrow_forwardA rock is thrown from the ground towards a building with an angle of 65 degrees above the horizontal line and with an initial velocity of 30m/s. The horizontal distance between where rock was thrown and the building is 45 meters. Find the speed of the rock right before it hits the building.arrow_forwardA rock is thrown off a cliff at an angle of 53° with respect to the horizontal. The cliff is 100 m high. The initial speed of the rock is 30 m/s. (a) How high above the edge of the cliff does the rock rise? (b) How far has it moved horizontally when it is at maximum altitude? (c) How long after the release does it hit the ground? (d) What is the range of the rock? (e) What are the horizontal and vertical positions of the rock relative to the edge of the cliff at t = 2.0 s, t = 4.0 s, and t = 6.0 s?arrow_forward
- A projectile is thrown from the top of a cliff with an initial speed of 25 m/s at an angle of 600 up from the horizontal. If the projectile lands 100 m from the base of the cliff how tall is the cliff?arrow_forwardA jumping frog is leaving the ground at an angle of 30° and with an initial speed of 4.62 m/s.(a) How high does the frog leap?(b) How far does the frog leap?arrow_forwardA rock is thrown horizontally with a speed of 20 m/ s from a vertical cliff of height 25 m. (a) Draw a sketch showing initial velocity of rock and vertical and horizontal displacement. (b) What are x and y components of initial velocity? (c) What are x and y components of acceleration? (d) How long does it take the rock to reach the horizontal ground below? (e) How far will it land from the base of the cliff?arrow_forward
- A stone is thrown from the top of a building upward at an angle of 30.0° to the horizontal and with an initial speed of 2.0 m/s, as shown in figure. If the height of the building is 45.0m, (a) how long is it before the stone hits the ground?arrow_forwardA stone is thrown from the top of a building upward at an angle of 30.0° to the horizontal with an initial speed of 20.0 m/s as shown. The height from which the stone is thrown is 45.0 m above the ground.(A) How long does it take the stone to reach the ground? (B) What is the speed of the stone just before it strikes the ground?arrow_forwardA baseball was hit with a speed of 30m/s at an angle of 45 degrees. It lands on the flat roof of a 13.0 m tall nearby building. If the ball was hit when it was 1.0 m above the ground, what horizontal distance does it travel before it lands on the building?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





