
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Among molecules mentioned in the question, it is to be determined which has shorter
Concept introduction:
Hybridization affects both bond length and bond strength. The two
Answer to Problem 3.27P
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the molecules mentioned in the question is shown below:
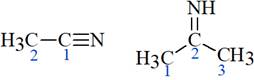
The two
In the first molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
In the second molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
This shows that in the first molecule, the percentage s character in
Bond length and bond strength is determined from the hybridization involved in the molecule.
(b)
Interpretation:
Among the molecules mentioned in the question, it is to be determined which has shorter
Concept introduction:
Hybridization affects both bond length and bond strength. The two
Answer to Problem 3.27P
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the molecules mentioned in the question is shown below:
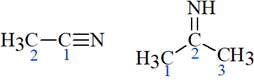
The two
In the first molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
In the second molecule, according to VSEPR theory, the
This shows that in the first molecule, the percentage s character in C-N bond is more than that in the second molecule. Therefore, the C-N bond is shorter and stronger in the first molecule.
Bond length and bond strength is determined from the hybridization involved in the molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Would each end of the bond line structure be carbon? Is problem (a) correct?arrow_forwardBelow are two sets of resonance structures. Where applicable provide the missing curved arrow notation, lone pair electrons, and nonzero formal charge. Do not delete or add any bonds or atoms.arrow_forwardGive only typing answer with explanation and conclusion What is the formal charge of the indicated atom?arrow_forward
- Need help with question a) Assign the geometry at each atom of molecule A, that has more than one bond, as tethrahedral, pyramidal, trigonal, angular, or linear. Explain your answersarrow_forwardDraw the major resonance structure for the compound shown; include lone pairs of electrons, formal charges, and condensed hydrogen atoms (located in the More menu). Then draw curved arrows to show how this can be converted to the Lewis structure givenarrow_forward(Answer with G explanation please give)arrow_forward
- Based on your answer to below Problem, do you thinkthe compound shown here should have a significantdipole moment? If so, in which direction does it point? The molecule shown here has quite a large dipole, asindicated in its electrostatic potential map. Explain why.Hint: Consider various resonance structures.arrow_forwardthe underlined atom has to be the center atomarrow_forwardDo either letter d), e) or a), c)arrow_forward
- Problem (1) Which of the following compounds show cis-trans isomerism? Draw the cis and trans isomers of those that do. CHF=CHF FC CH2 CH;=CH-CH,-CH3 -CHCH, -CHCHCH, CHCH,arrow_forwardIdentify all functional groups that are present in strychnine, a highly toxic alkaloid used as a pesticide to kill rodents, whose line structure is shown here. What compound class is characteristic of each of those functional groups? Strychninearrow_forward(a) Draw all valid resonance contributors for this iIon. Show how the electrons can be moved using curved arrOWs. (b) Draw the resonance hybrid.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





