
Concept explainers
Still referring to Problem 1, what will be the possible genotypes of offspring from the following matings? With what frequency will each genotype show up?
- a. AABB × aaBB
- b. AaBB × AABb
- c. AaBb × aabb
- d. AaBb × AaBb
a.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AABB × aaBB.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AABB and aaBB.
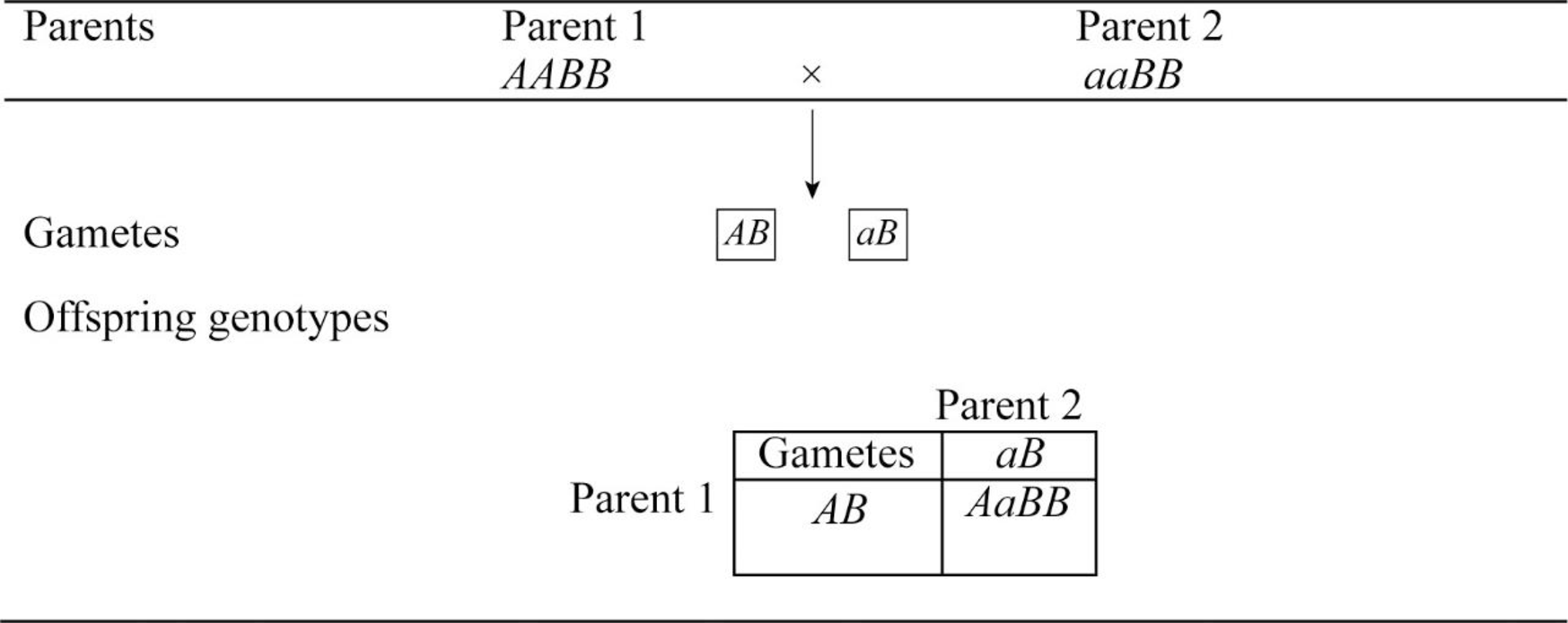
All the offspring have the same genotype AaBB. Therefore, there is no genotype frequency.
b.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AaBB × AABb.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AaBB and AABb.
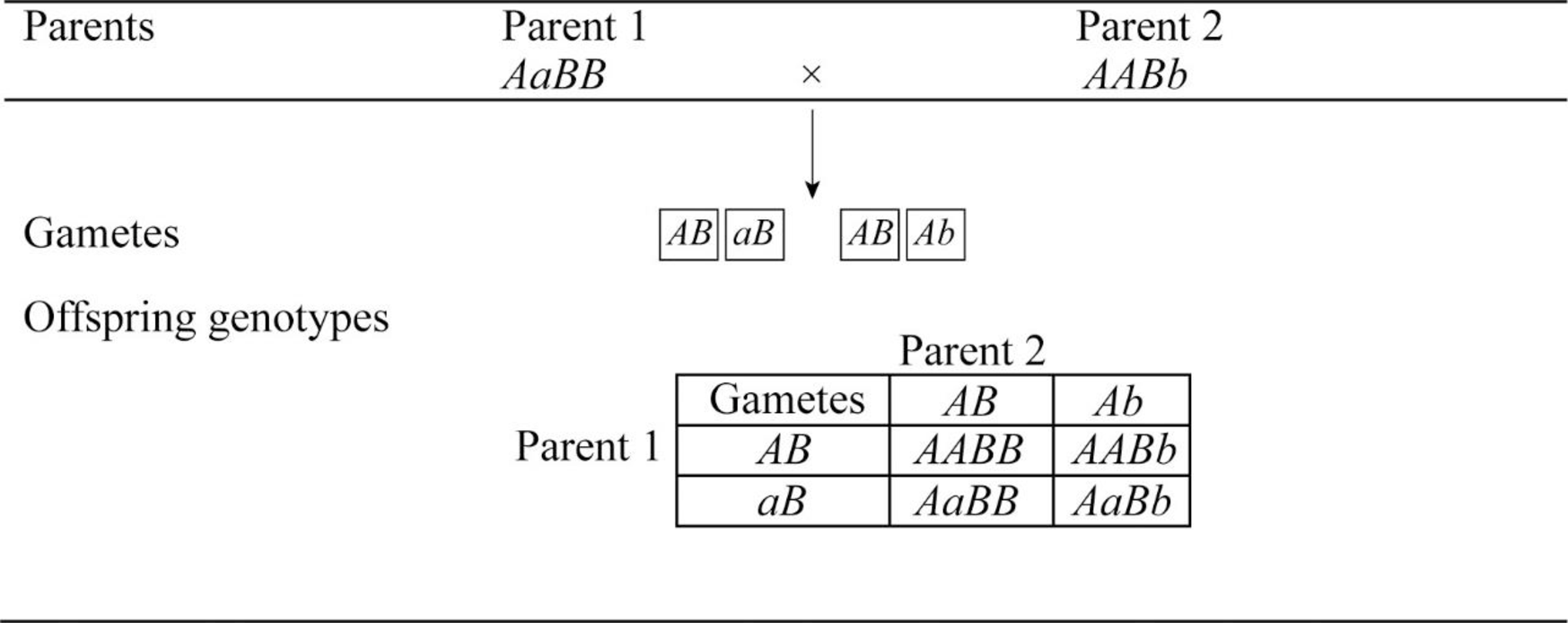
The following is the frequency of genotypes.
Total number of possible genotypes = 4.
AABB=
AABb=
AaBB=
AaBb =
The frequency of all four genotypes is 25%.
c.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AaBb × aabb.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AaBb and aabb
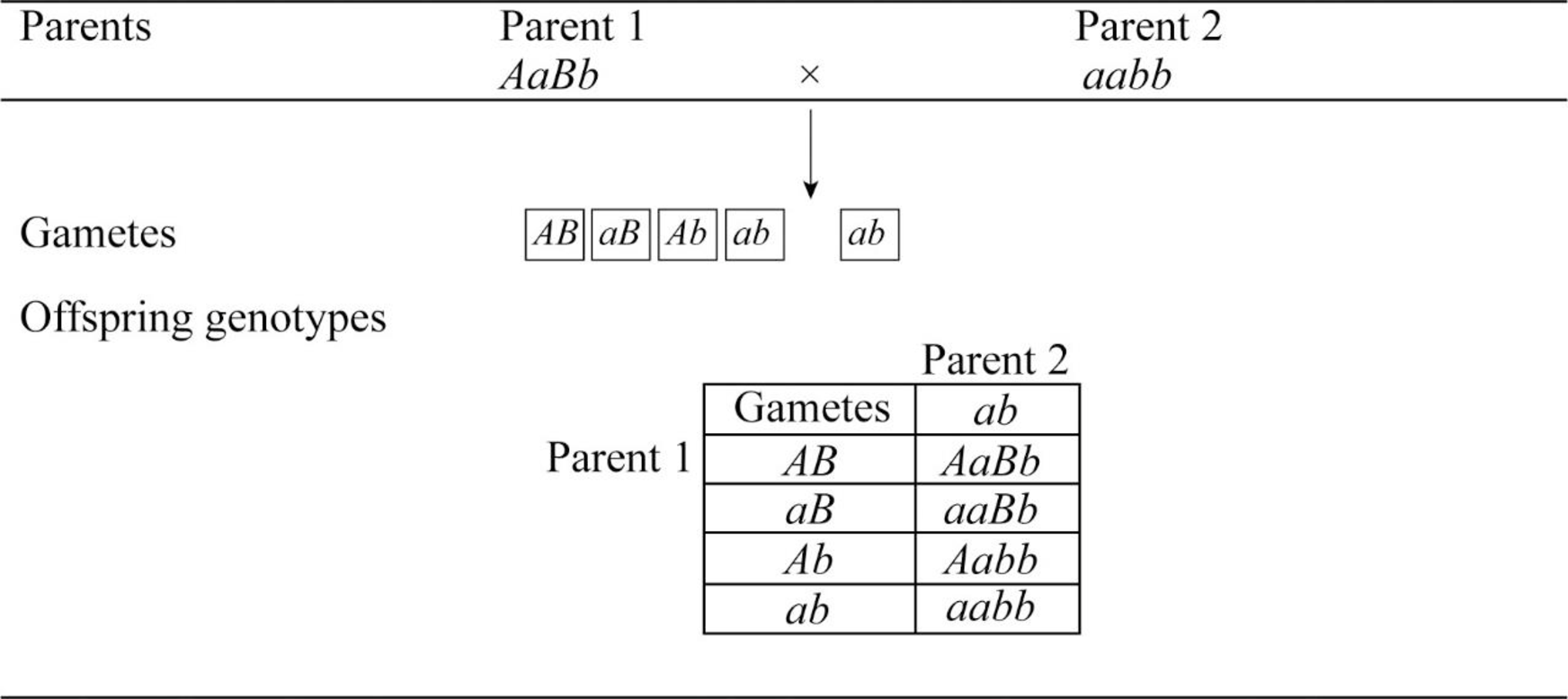
The following is the frequency of genotypes.
Total number of possible genotypes = 4.
AABB=
aaBB=
Aabb=
aabb =
The frequency of all four genotypes is 25%.
d.
To predict: The predicted genotype frequencies among the offspring for the mating AaBb × AaBb.
Introduction: The law of independent assortment and law of segregation are the laws proposed by Gregor Johann Mendel, a geneticist. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of monohybrid cross that “two alleles at any locus tend to separate from each other during meiosis, so they end up in different gametes”. Mendel proposed the law of independent assortment based on the results of dihybrid cross that “alleles at one locus tend to assort into gametes independently of alleles at other loci”. The number of possible allele combination for the given genotype is given by the formula 2n where “n” is the number of heterozygous alleles that are present.
Explanation of Solution
A monohybrid cross is constructed with Punnett square for the parents having the genotype AaBb and AaBb.
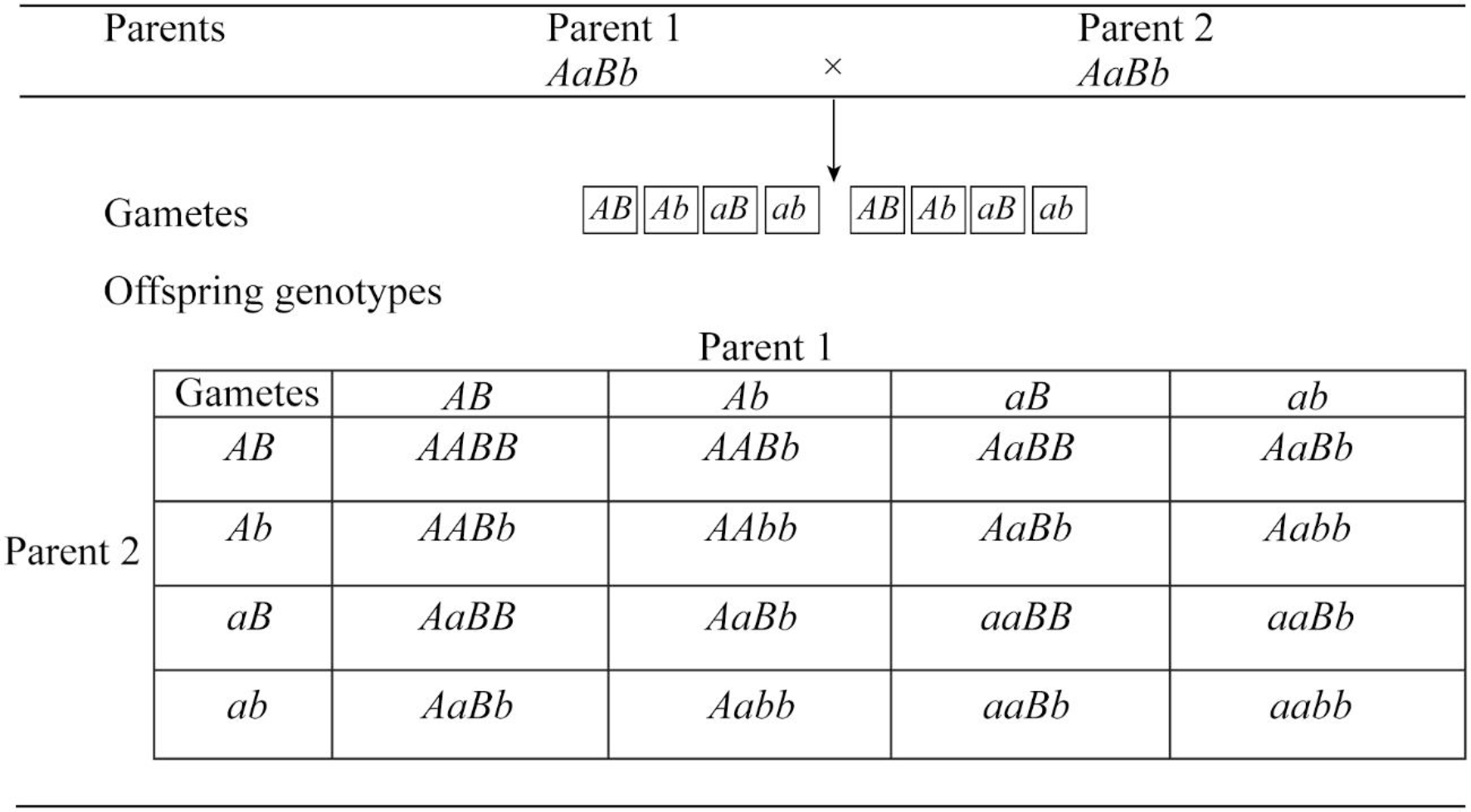
The following is the frequency of genotypes.
Total number of possible genotypes = 16.
AABB=
AABb=
AaBB=
AaBb=
AAbb=
Aabb=
aaBB=
aaBb=
aabb=
The frequency of genotypes AABB, aaBB , AAbb and aabb is 6.25%.
The frequency of genotypes AaBB, AABb, aaBb and Aabb is 12.5%.
The frequency of genotypes AaBb is 25%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
EBK HUMAN BIOLOGY
- A. Select and assign symbols for the genes involved, and determine the genotypes of the parents and offspring in each cross. Pigeons may exhibit a checkered or plain color pattern. In a series of controlled matings, the following data were obtained. F1 Progeny P1 Cross Checkered Plain 1. (a) checkered x checkered 36 0 2. (b) checkered x plain 38 0 3. (c) plain x plain 0 35 Then F1 offspring were selectively mated with the following results. (The P1 cross giving rise to each F1 pigeon is indicated in parentheses.) F2 Progeny F1 x F1 Cross Checkered Plain 4. checkered (a) x plain (c) 34 0 5. checkered (b) x plain (c) 17 14 6. checkered (b) x checkered (b) 28 9 7. checkered (a) x checkered (b) 39 0arrow_forwardRead in your textbook about positive assortative mating. In this example, from your text, positive assortative mating is 100% (i.e. there is no random mating). Note that the frequency of heterozygotes is cut in half each generation. Does this match your answers above? Look at the actual values make sure you understand why positive assortative mating leads to an increase in homozygosity. (a) Only heterozygotes produce heterozygote offspring, but only 50% of the time Homozygote parent for A, Heterozygote parent Homozygote parent for A, Eggs A, A, Eggs A2 A, Eggs A2 A2 A, A, A, A, A, A, A, A, A, A2 A2 A2 A2 A2 A2 A, A, A, A, A, A, A, A2 A2 A2 A2 A2 Az A2 A2 (b) Effect of extreme inbreeding (self- fertilization) over time A, A, Homozygote A, A2 Heterozygote A2 A2 Homozygote The arrows represent A, p= 0.5 offspring genotypes that are produced by each parental genotype Generation 1 Az q = 0.5 100% 25% 50% 25% 100% A, p= 0.5 Az q= 0.5 Generation 2 100% 25% 50% 25% 100% The frequencies of…arrow_forwardExcessive secretion of male sex hormones results in premature sexual maturation in males and masculization of the sex characters in females. This disorder is called the adrenogenital syndrome, and in Switzerland there is an autosomal recessive form of the disease that affects about one in 5000 newborns. a. Assuming random mating, what is the allele frequency of the recessive? b. What is the frequency of heterozygous carriers?arrow_forward
- 4) The round pea seed allele (R) is dominant, while the wrinkled pea seed allele (r) isrecessive. A heterozygous round-seeded pea plant is crossed with a wrinkle-seeded peaplant. Use a Punnett Square to solve the following: a. Determine the predicted genotype ratio of the offspring. b. Determine the predicted phenotype ratio of the offspring. c. If this cross produced 50 plants, how many plants would you predict would bewrinkle-seeded pea plants? please if punnet square needed write down the P G and F1 also thanksarrow_forwardIn a diploid plant species, an F1 with the genotype Mm Rr Ss is test crossed to a pure breeding recessive plant with the genotype mm rr ss. The offspring genotypes are as follows: Genotype Number Mm Rr Ss 687 Mm Rr ss 5 Mm rr Ss 68 Mm rr ss 196 mm Rr Ss 185 mm Rr ss 72 mm rr Ss 8 mm rr ss 679 Total 1900 1. What is the interference value for this data set?arrow_forwardYou have determined that the gene order for three linked genes being studied is CBA. The number of recombinants resulting from crossover between genes A and B alone totals 40 and 42, while the double-crossover progeny total 4 and 6. What is the recombination frequency between genes A and B if the total number of progeny from the cross is 1000? O 0.102% O 0.092% O 10.2% O 0.082% O 8.2% O 1% O 9.2%arrow_forward
- Consider a situation where F1 is backcrossed with one of its parental lineage and we obtained A1H1/A2H2 : A2H1/A2H2 : A2H2/A2/H2: A1H2/A2H2 = 295 : 186 : 310 : 209, where A1 and A2 are alleles at a locus and H1 and H2 are alleles at the other locus. What is the recombination (genetic) distance between the two loci in centimorgans? A. 8.9 B. 22.5 C. 18.4 D. 50 E. 39.5arrow_forwardThe genotype of F1 individuals in a tetrahybrid cross is AaBbCcDd X AaBbCcDd. Assuming independent assortment of these four genes, what are the probabilities that F2 offspring will have the following genotypes? Calculate the probability of each using multiplication and addition rules. Show your work. a. aabbccdd b. AaBbCcDd c. AaBBCCdd d. Any of the 3 genotypes abovearrow_forwardHeterozygous Cc chickens express a condition called creeper, in which the leg and wing bones are shorter than normal (cc). The dominant C allele is lethal when homozygous. Skin color is determined by the alleles W and w. W_ chickens have white skin and ww chickens have yellow skin. In a mating between 2 chickens heterozygous for both of these genes: 1) What phenotypes will be observed in the progeny? 2) What fraction of the offspring will have each phenotype? Assign alleles. List possible phentoypes. Make gametes, draw Punnett square, and list fractions of genotypes and/or phenotypes of offspring,arrow_forward
- Answer the following with a short solution if needed: a. The gametes of a worm's genotype SsYy should produce what genotypes? b. A genetic cross between two F1-hybrid rose plants having yellow petals will yield what percent green-petal plants in the F2 generation? Yellow petals are dominant to green. c. Brown fur is dominant over light-colored fur. What is the phenotype of the resulting offspring if you cross a heterozygous brown fur and a light-colored fur?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is the best statement of the use of the addition rule of probability? Select one: a.the probability that either one of two independent events will occur b.the probability of producing two or more heterozygous offspring c.the likelihood that a trait is due to two or more meiotic events d. the probability that two or more independent events will both occur in the offspring of one set of parents e.the probability that two or more independent events will both occurarrow_forwardA is dominant over a and B is dominant over b. Genes A/a and B/b assort independently. The parental cross (P) is between true- breeding (homozygous) strains (AA bb x aa BB). The resulting F1 offspring would be [Select ] A F1 x F1 cross gives the F2 generation. The ratio of phenotypes in the F2 generation can be described as [ Select ] In the phenotypic ratio, what number refers to individuals that are: dominant for both traits? [ Select ] recessive for both traits? [Select ] To what phenotypes do the "3"s in the ratio refer? [ Select ] > >arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
