
Concept explainers
A
Figure 16.6. What is the structure of this diol?
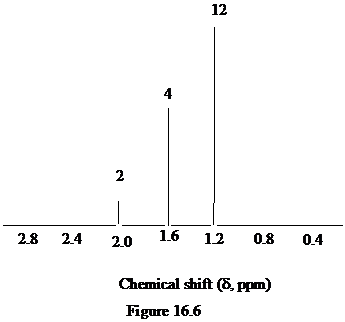
Interpretation:
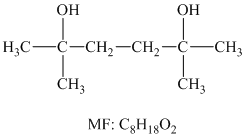
The structure for the diol having molecular formula
Concept introduction:
The vicinal diols on treatment with periodic acid
The oxygen atoms do not show any effect on the index of hydrogen deficiency.
The index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) represents the presence of number of multiple bonds or a ring in a molecule which can be calculated from the following formula,
Here,
The
The chemical shift for the protons at carbon bonded to electron withdrawing group increases due to de-shielding effect.
Answer to Problem 36P
Solution: The structure for the diol having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
As it is mentioned that the diol having molecular formula
As the oxygen atoms have no effect on index of hydrogen deficiency, the molecular formula of the given compound can be written as
Thus, the index of hydrogen deficiency in the given molecule can be calculated as follows:
This shows that the molecule does not have a ring or multiple bond. It is saturated compound.
The approximate chemical shift values from the given
a)
b)
c)
The arrangement of atoms in a molecule form the given chemical shift values are as follows:
The chemical shift at
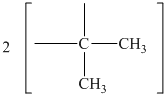
The peak at
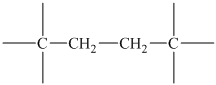
The peak at
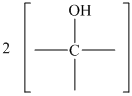
Hence, the structure of diol having molecular formula
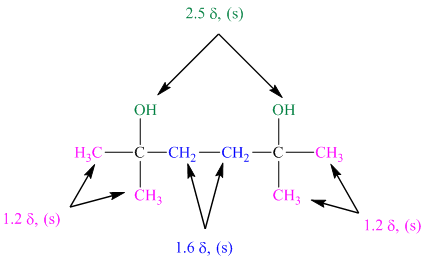
The structure of diol having molecular formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Several diamines are building blocks for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agro-chemicals. Show how both 1,3-propanediamine and 1,4-butanediamine can be prepared from acrylonitrile.arrow_forwardExplain why p-nitrophenol is more acidic than 4- nitrocyclohexanol?arrow_forwardWhich of the following reagents will convert salicylic acid into acetyl salicylic acid? HO HO, OCCH3 ethanol H2SO4 benzoic anhydride Methanol H2SO4 acetic anhydride thionyl chloridearrow_forward
- What product is formed from the addition of NaOH to p-tertbutylphenol? Group of answer choices a compound with addition of an OH group to p-tertbutyl phenol the sodium salt of p-tertbutylphenol, sodium p-tertbutylphenoxide a protonated version of p-tertbutylphenol there is no reactionarrow_forward4-Methylphenol is more acidic than ethanol (pKa 10.36 vs 16.0) , even though both contain an OH group and a methyl group. Draw the structures of the anions formed from loss of the alcoholic protons from both compounds. Use resonance to explain the difference in their respective acidities.arrow_forwardIdentify the best reagents to complete the following reaction. Options are included.arrow_forward
- The 1H and 13C NMR spectra below belong to a compound with formula C6H10O2. Propose a structure for this compound.arrow_forwardCompound H (C8H6O3) gives a precipitate when treated with hydroxylamine in aqueous ethanol and a silver mirror when treated with Tollens solution. Following is its 1H-NMR spectrum. Deduce the structure of compound H.arrow_forwardRank the following substances in order of increasing acidity: (a) (CH3)2CHOH, HC≡CH, (CF3)2CHOH, CH3OH (b) Phenol, p-methylphenol, p-[trifluoromethyl) phenol (c) Benzyl alcohol, phenol, p-hydroxybenzonic acidarrow_forward
- Propose a structural formula for each compound consistent with its 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra. (a) C5H10O2 (b) C7H14O2 (c) C6 H12O2 (d) C7H12O4 (e) C4H7ClO2 (f) C4H6O2arrow_forwardClaisen condensation between diethyl phthalate and ethyl acetate followed by saponification, acidification, and decarboxylation forms a diketone, C9H6O2. Propose structural formulas for compounds A and B and the diketone.arrow_forwardWhich of the following aromatic compound has a hydroxy substitution? There can only be 1 answer. a Aniline b Cresol c Phenol d Toluenearrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


