
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron-pair geometry for the molecules
Concept introduction:
The electron pairs in Lewis diagrams repel each other in real molecule and thus they distribute themselves in positions around the central atoms that are as far away from one another. This arrangement of electron pairs is called electron-pair geometry. The electron pairs may be shared in covalent bond, or they may be lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 21E
The Lewis diagrams for
![]() ,
, 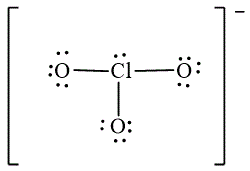 and
and 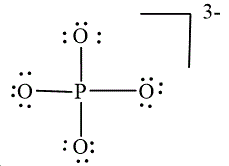
The wedge-and-dash diagrams for
![]() ,
, 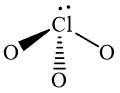 and
and 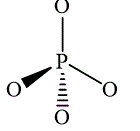
The electron pair geometry for
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule,
In the molecule,
Similarly, in the molecule
The atom which is least electronegative is the central atom. In
![]()
Figure 1
In

Figure 2
In

Figure 3
The electron-pair geometry depends on the number of electron pairs around the central atom. In the molecule
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
![]()
Figure 4
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
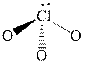
Figure 5
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
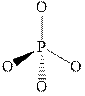
Figure 6
The Lewis and wedge-and-dash diagrams for
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular geometry prdicted by the valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory for the molecules
Concept introduction:
Molecular geometry is the precise term that is used to describe the shape of molecules and arrangement of atoms around the central atom. The molecular geometry of a molecule is predicted by valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory or in short VSEPR theory. VSEPR theory applies to substances in which a second period element is bonded to two, three, four, or other atoms.
Answer to Problem 21E
The Lewis diagrams for
![]() ,
,  and
and 
The wedge-and-dash diagrams for
![]() ,
,  and
and 
The molecular geometry for
Explanation of Solution
To write the Lewis diagram for a compound first the number of valence electrons is to be calculated. In the molecule,
In the molecule,
Similarly, in the molecule,
The atom which is least electronegative is the central atom. In
![]()
Figure 1
In

Figure 2
In

Figure 3
The molecular geometry depends on the number of electron pairs around the central atom and the number of lone pair on the central atom. In the molecule
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules
![]()
Figure 4
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules

Figure 5
The wedge-and-dash diagram for the molecules

Figure 6
The Lewis and wedge-and-dash diagrams for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Which statements are true about electronegativity? (a) Electronegativity increases from left to right in a period of the Periodic Table. (b) Electronegativity increases from top to bottom in a column of the Periodic Table. (c) Hydrogen, the element with the lowest atomic number, has the smallest electronegativity. (d) The higher the atomic number of an element, the greater its electronegativity.arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about the shape of the bromine pentafluoride (BrF, molecule. How many electron groups are around the central bromine atom? Note: one "electron group" means one lone pair, one single bond, one double bond, or one triple bond. What phrase best describes the arrangement of these electron groups around the central bromine atom? (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) (choose one)arrow_forwardQUESTION 5 Determine which compound should have a(n) linear molecular geometry. Key Concept: Lewis structures are drawn from a knowledge of the total number of electrons from all the atoms involved in the structure. The element with the lowest electronegativity is the central atom. Fulfill octet of outside atoms first. Molecular shape depends upon the number of atoms and lone pair electrons around the central atom. A H3O+ B ClF2+ C IF2- D AsF5arrow_forward
- Use Lewis theory to determine the formula for the compound that forms between each of the following pairs of elements. Ca and I Express your answer as a chemical formula. Na and Se Express your answer as a chemical formula. Al and O Express your answer as a chemical formula.arrow_forwardWrite the Lewis structure for the following molecule. State the electronic structure (shape based on electron pairs or bonds) AND the geometric structure (shape based on the atoms only). Include all valence electrons in your structure. State how many electrons are used to form covalent bonds in the molecule. Is the molecule polar? O2arrow_forwardQuestion 9 which of the following molecules has a net dipole moment? consider any molecule with resonance structures to be the average of all resonances co,2 O NH4 O CHOCI CO2arrow_forward
- Consider the following ion: BrO3 − . a) Show the full electron configuration for Br. b) Draw the most correct Lewis structure for BrO3 − and briefly explain why your Lewis structure is correct. c) If the structure is stabilised by resonance, draw at least one of the possible resonance forms. If it is not stabilised by resonance, briefly explain why. d) What is the electronic geometry of BrO3 − ? What is its molecular shape? e) Does BrO3 − have a dipole moment? Briefly justify your answer. f) On average, would you expect IO3 − to have longer or shorter bonds than BrO3 − ? Briefly explain your answer. g) Which of the following molecules would you expect to have the lowest vapour pressure? Briefly explain your choice. h) What is the molecular formula for Compound C? What is the empirical formula for Compound C?arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about the shape of the phosphorus tetrafluoride (PF ) anion. How many electron groups are around the central phosphorus atom? Note: one "electron group" means one lone pair, one single bond, one double bond, or one triple bond. What phrase best describes the arrangement of these electron groups around the central phosphorus atom? (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) v (choose one) linear bent T-shaped trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal square planar square pyramidal tetrahedral sawhorse trigonal bipyramidal octahedral Oarrow_forwardDraw a Lewis structure for the following ions/molecules, including any resonance structures and/or formal charges. Place a box around any contributing resonance structures XeO4^-2, BrF5, CHF2CL What is the electron group geometry around the central atom for each of the above ions/molecules? For the above ions/molecules, what is the shape of the entire molecule/ion of the entire ion/molecule? Identify polar bonds with dipole arrows Indicate whether each of the ions/molecules is POLAR or NON-POLARarrow_forward
- Answer the questions in the table below about the shape of the phosphorus trifluoride (PF3) molecule. How many electron groups are around the central phosphorus atom? Note: one "electron group" means one lone pair, one single bond, one double bond, or one triple bond. What phrase best describes the arrangement of these electron groups around the central phosphorus atom? (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) (choose one) X Śarrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about the shape of the sulfur hexabromide (SBr) molecule. How many electron groups are around the central sulfur atom? Note: one "electron group" means one lone pair, one single bond, one double bond, or one triple bond. What phrase best describes the arrangement of these electron groups around the central sulfur atom? (You may need to use the scrollbar to see all the choices.) (choose one) X Ś Um 0 Garrow_forwardWrite the Lewis structure for molecule or ion. O2 2-arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
