
The characteristic frequencies of the two coupled oscillators with all spring constants different, and to compare it with the natural frequencies of the two oscillators in the absence of coupling.
Answer to Problem 12.1P
The characteristic frequencies of the two coupled oscillators with all spring constants different are
Explanation of Solution
The system of the two coupled oscillators with all spring constants different are shown in Figure 1.
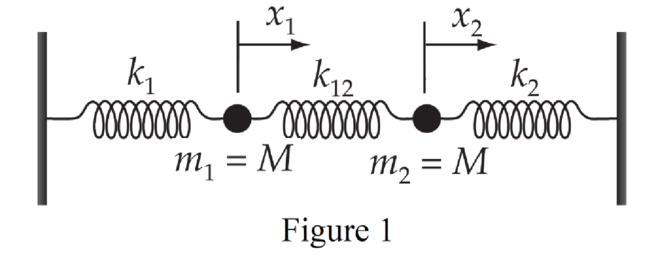
In the figure, the spring constants of the springs are marked as
Write the equations of motions for the system.
Let us attempt the solutions of the form;
Here,
Use the solutions in (II) in (I).
The condition for obtaining a non-trivial solution is that, the determinant of the coefficients of
Solve equation (IV) to get an expression for
Thus, the characteristic frequencies will be;
Consider the case;
If the mass
If the mass
Comparing equation (VI) and (VII) with the two frequencies given by equation (V), it can be observed that;
Similarly;
From equation (IX) and (X) it is clear that;
If
Conclusion:
Therefore, the characteristic frequencies of the two coupled oscillators with all spring constants different are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
- Problem 5: Consider a 1D simple harmonic oscillator (without damping). (a) Compute the time averages of the kinetic and potential energies over one cycle, and show that they are equal. Why does this make sense? (b) Show that the space averages of the kinetic and potential energies are (T)₂ = k1² KA² and (U),= KA². Why is this a reasonable result?arrow_forwardWhat is the curl of the linear restoring force for an isotropic harmonic oscillator?arrow_forwardQ.3 (a) Measurements conducted on a servomechanism show the systemresponse to be:C (t) = 0.3 e60t + 1.5 e10t , when subjected to a unit step input.[1].Obtain the expression for the closed-loop transfer function.[2].Determine the undamped natural frequency and damping ratio of thesystem. Q.3 (b) A Tank system having a time constant of 0.5 min and a resistance of0.25 min /m2 is operating at steady state with an inlet flow of 2m3/min. Theflow is suddenly increased to 3m3/min. Plot the response of the tank level(Assume area of cross section A = 2 m2). Q.3 (c) Describe the Hardware elements of a process control system.Differentiate the process lag and control lag with suitable example.arrow_forward
- A sphere, of radius a, is suspended by a fine wire from a fixed point at a distance I from its centre show that the time of a small oscilation is given by 2π 2x -√√(5¹²2+ 20°) { 1 + ½ sin² (2)}, where a represents the ar "tude of the vibration.arrow_forwardA mass of 12 slugs is hanging at rest on a frictionless spring whose constant is k = 1/3 . Beginning at time t = 0, an external force of F(t) = 20cos(ωt) is applied to the system. (a) What is the angular frequency of the forcing function that is in resonance with thesystem?(b) Find the equation of motion of the mass with resonance.arrow_forwardThe spool has a mass, m, and a radius of gyration, kG. The inextensible cord is attached to the wall at A. The cord is wound around the radius R, and the out radius 2R. The coefficient of friction between the ground and the spool is mu. Given the quantites given, m, kG, R, and mu, write the solution in terms of the given quatities. Find the critical force (force required to cause motion) Fcrit. The force is applied at point B. See attached drawing. Let the force be 2Fcrit. What is the linear acceleration of the center of mass? If the force is 2Fcrit, what is the tension in the cord AC?arrow_forward
- Prob.1 (i) State the required conditions of simple harmonic motion (SHH). (ii) Consider the torsional pendulum with a moment of inertia l and torsion constant K. If the pendulum starts its oscillation with an initial angle Oi and angular de velocity wj at t = 0. Obtain the equation of motion and angular frequency of dt oscillation w. for this pendulum and discuss that it can be classified as SHH. (iii) Show that the torsional angle and angular velocity o of the pendulum for all time can be expressed as O(t) = 0; cos wt + sin wt w(t) = -w0; sin wt +w¡ cos wt .arrow_forwardQuestion 1. Find the steady state solution of the forced Mass-Spring-Damper with the following parameters undergoing forcing function F(t). 3 kg, c = 22 Ns/m, k = 493 N/m, F(t) = 21 cos(6t) in the form of (t) = A cos(6t – 8) Enter your answers for A and to four decimal places in the appropriate boxes below: m = A: d:arrow_forwardProb.1 (i) State the required conditions of simple harmonic motion (SHH). (ii) Consider the torsional pendulum with a moment of inertia I and torsion constant K. If the pendulum starts its oscillation with an initial angle O, and angular at t = 0. Obtain the equation of motion and angular frequency of dt de velocity j %3D oscillation w. for this pendulum and discuss that it can be classified as SHH. Show that the torsional angle and angular velocity a of the pendulum for all time can be expressed as (iii) sin wt 0 (t) = 0; coS wt + w(t) = -w0; sin wt + w cos wt .arrow_forward
- A uniform rod of mass M and length L is free to swing back and forth by pivoting a distance x from its center. It undergoes harmonic oscillations by swinging back and forth under the influence of gravity.Randomized Variables M = 2.4 kgL = 1.6 mx = 0.38 m a) In terms of M, L, and x, what is the rod’s moment of inertia I about the pivot point. b) Calculate the rod’s period T in seconds for small oscillations about its pivot point. c) In terms of L, find an expression for the distance xm for which the period is a minimum.arrow_forwardConsider a small mass performing simple harmonic motion with angular frequency 10 rad/s. If we know that at t = 0 the mass is at ro = +5 cm moving to the right at +87 em/s, and we want to represent the oscillations using a cos function then.. (a) Find the amplitude of the oscillations (b) Find the phase constant of the oscillations (c) Find the maximum speed of the mass (d) Find the maximum acceleration of the massarrow_forwardA spring of rest length La (no tension) is connected to a support at oneend and has a mass M attached at the other. Neglect the mass of the spring, the dimension of the mass M, and assume that the motion is confined to a vertical plane. Also, assume that the spring only stretches without bending but it can swing in the plane. (a) Using the angular displacement of the mass from the vertical and thelength that the string has stretched from its rest length (hanging with themass m), find Lagrange’s equations. (b) Solve these equations for small stretching and angular displacements.arrow_forward
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
