
Biology
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781260487947
Author: BROOKER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 58.5, Problem 1CS
Core Skill: Connections In the two food chains illustrated in Figure 58.13, plants and protists (phytoplankton) are the producers. Refer back to Section 27.4. What other organisms are producers and could also support food chains?
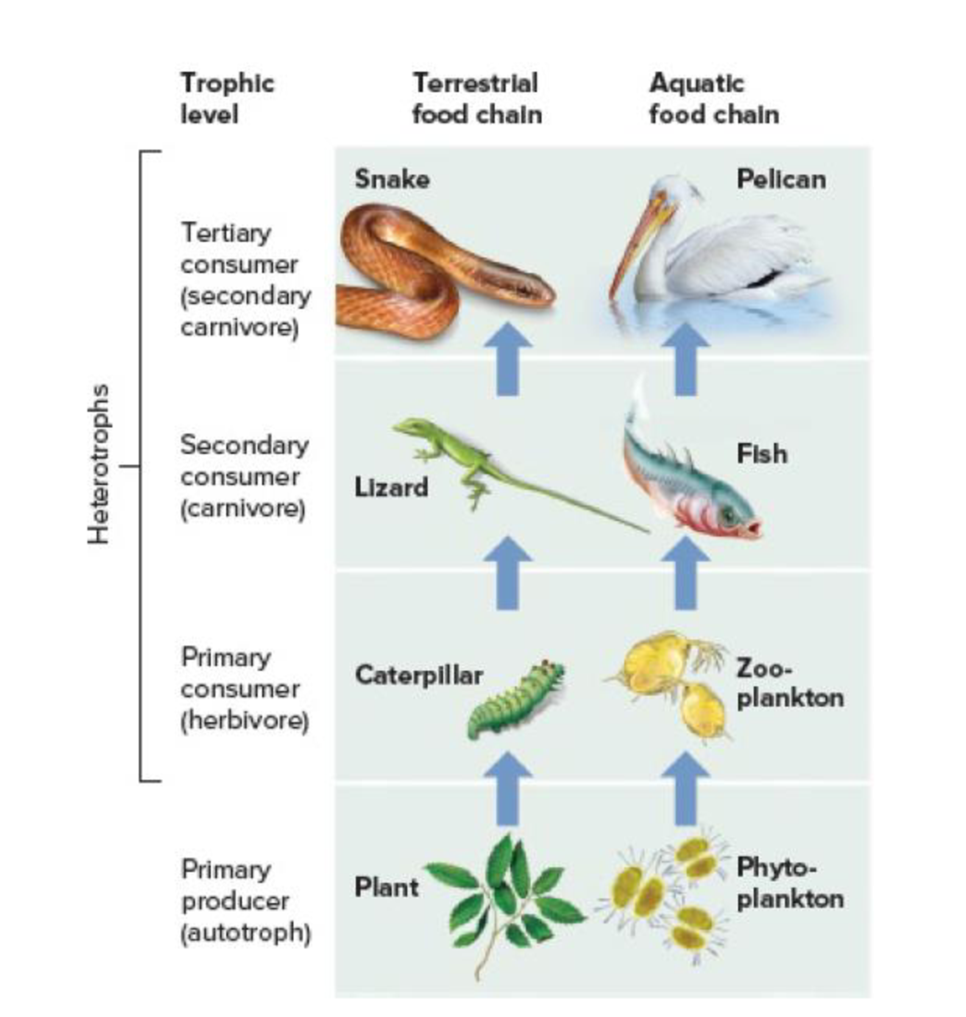
Figure 58.13 Food chains. Two examples of the flow of food energy up the trophic levels: a terrestrial food chain and an aquatic food chain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Name
Worksheet- Food Chain and Food Web
Part 1 "Food Chain"
Date
Per
Instructions: Fill in the blanks as
directed below
1. Label each feeding level correctly:
(Trophic Levels = 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th)
2. Label each correctly: producer,
consumer (primary, secondary, tertiary)
3. What type of feeding habit does each
organism have (producer, herbivore,
carnivore, omnivore, decomposers)
Solar
Fox
Bed
4. What is the purpose (job, niche)
of the decomposers:
Suntiowers
Caterpillar
Decomposers
Ibacteria and fungi
Part 2 "Food Web"
Instructions: Fill in the blanks as directed below
1. Label each feeding level correctly:
(Trophic Levels = 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th)
5 x
core.learn.edgenuity.com/player/
+
ence- SC5181 A
↑
3
2
Mark this and retum
C
6 7 8
Which of the following is a valid comparison of the net primary productivity of a salt marsh to the net primary productivity of the ocean?
O The salt marsh has a higher net primary productivity because it is smaller in area and volume.
O The salt marsh has a higher net primary productivity because it has higher salinity
O The ocean has a higher net primary productivity because it is larger in area and volume
O The ocean has a higher net primary productivity because it has more organisms producing carbon.
0
%
5
омо
A
6
Oll
DELL
&
7
O
*
8
O
Save and Exit
(
9
)
O
Next
<☆
English
4
Submit
Oct 7
Kinley Heath
40
LO X
□:
2:04 0 D
+
=
(
backspa
Hypothetical balanced food chain. Sun and Earth supply 6 units of energy to each plant. For higher tropic levels, individuals consume 2 units of energy each before passing the remainder to the next trophic level. The number of individuals in each trophic level is given below. Complete the table below by computing for the number of energy units in each column. Answer the following questions:
Discuss how the food chain works.
Where does each trophic component or level get its energy (food) from?
What is the ultimate source of energy for all components of the food chain?
Which component got the highest amount of available energy/individual?
Why do members of this component need the most energy?
Chapter 58 Solutions
Biology
Ch. 58.1 - Prob. 1CCCh. 58.3 - Prob. 1CCCh. 58.3 - Inhibition implies that competition exists between...Ch. 58.4 - Prob. 1CSCh. 58.4 - Prob. 1CCCh. 58.4 - Prob. 1EQCh. 58.4 - Prob. 2EQCh. 58.4 - CoreSKILL What did the researchers conclude about...Ch. 58.5 - Core Skill: Connections In the two food chains...Ch. 58.5 - Prob. 1CC
Ch. 58.5 - Prob. 2CSCh. 58 - Prob. 1TYCh. 58 - Prob. 2TYCh. 58 - Which evidence suggests that more diverse...Ch. 58 - The process of primary succession occurs a. around...Ch. 58 - Prob. 5TYCh. 58 - Prob. 6TYCh. 58 - Prob. 7TYCh. 58 - Prob. 8TYCh. 58 - Prob. 9TYCh. 58 - Prob. 10TYCh. 58 - Prob. 1CQCh. 58 - Prob. 2CQCh. 58 - Core Concept: Systems In the nutrient-poor...Ch. 58 - List some possible ecological disturbances, their...Ch. 58 - Prob. 2COQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A conceptual model representing the role, interaction, reaction, and density of essential ecosystem components is shown below. Examine the model and the relationships between the major players (i.e., predator, prey, producer). The structure's most important role is played by these major players. It's also worth noting that nutrition has been included in the model. This is the abiotic component that has a direct or indirect impact on the interaction. Question: Why does the organism’s interaction appear in an oscillating pattern? What does it suggest?arrow_forwardThe average efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels is 10%. Use this efficiency to determine how much phytoplankton mass is required to add just 1 gram (0.04 ounce) of new mass to a killer whale, which is a third-level or top carnivore. Create a diagram that summarizes the different trophic levels and the relative size and abundance of organisms at each level. How would your answer change if the efficiency were half the average rate? Twice the average rate?arrow_forwardConstruct your model of the food chain/web by moving and linking (using arrows leading from those that eat and those that are eaten) all 8 images of the different species (trophic components).arrow_forward
- Create a model which accurately, in detail, depicts the potential pathways of carbon (biomass) and energy in an ecosystem with at least five trophic levels (don’t forget your decomposers, they can count as one trophic level). Make sure to incorporate the multiple pathways that biomass and energy could take at each trophic level. Lastly, clearly illustrate how carbon and energy flow in this ecosystem. Be sure to include adequate levels of detail for all pathways and differentiate the flow of carbon and energy in your model.arrow_forwardHypothetical balanced food chain. Sun and Earth supply 6 units of energy to each plant. For higher tropic levels, individuals consume 2 units of energy each before passing the remainder to the next trophic level. The number of individuals in each trophic level is given below. Complete the table below by computing for the number of energy units in each column and answer the questions below.arrow_forwardhttps://www.biointeractive.org/classroom-resources/exploring-trophic-cascades create a case study based on additional research into other examples of trophic cascades. describe and illustrate how changes in an organismal population can have unintended effects on trophic levels or ecosystems. Identify the organisms and nutrients (if applicable) that are present in your trophic pyramid. Describe the normal flow of your trophic cascade along with whether removal or introduction of the organism has a positive or negative effect on other organisms or nutrient levels within an ecosystem.arrow_forward
- Discuss how the food chain works. Where does each trophic component or level get its energy (food) from?arrow_forwardA conceptual model representing the role, interaction, reaction, and density of essential ecosystem components is shown below. Examine the model and the relationships between the major players (i.e., predator, prey, producer). The structure's most important role is played by these major players. It's also worth noting that nutrition has been included in the model. This is the abiotic component that has a direct or indirect impact on the interaction. Question: Based on this scenario, what is the most significant role of sea otters in the marine community? Why it’s important?arrow_forwardOrganisms at a higher trophic level have less energy available.comment.arrow_forward
- How would you describe the trophic levels in a typical ecosystem? Discuss the flow of energy through the ecosystem, the relationship between the different trophic levels, and the factors that limit the number of trophic levels.arrow_forwardHypothetical balanced food chain. Sun and Earth supply 6 units of energy to each plant. For higher tropic levels, individuals consume 2 units of energy each before passing the remainder to the next trophic level. The number of individuals in each trophic level is given below. Complete the table below by computing for the number of energy units in each column. Trophic Levels No. Individuals in Each Trophic Level No. of Units Received from Trophic Level Above No. Units Used / Individual (Resp) No. Units Used in Trophic Level No. Units Remaining & Passed on to Next Trophic Level Mean No. Units Available per Individual in Trophic Level SUN +E = 6 1) Plants 30 180 2 2) Grasshopper 19 2 3) Frog 12 2 4) Snake 8 2 5) Owl 4 2arrow_forwardIn the trophic structure, autotrophs are living organisms that: Are at the top of the chain, referred to as tertiary producers. Photosynthetic organisms that produce their own energy Organisms that receive their energy by consuming producers such as plants Help to decompose the remains of dead organismsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education
Ecology: Interspecific and Intraspecific Interactions | Ecology & Environment | Biology | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IiQTrA0-TE8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY