Consider the market for a particular brand of watch, illustrated in the figure to the right. Suppose there are network externalities in this market such that the quantity of the good demanded falls in response to the growth of purchases by other individuals (as indicated by the demand curve "Demand" in the figure). Suppose that the price is initially $14,000 where the quantity demanded is 60 watches per month. 18000- 16000- 14000- E3 12000- If the price of this brand of watch falls to $10,000, demand will increase to watches. (Enter your response using an integer.) However, without negative network externalities, demand would have increased by ☐ units, which is the pure price effect, meaning the size of the snob effect is (Enter your responses using integers.) The snob effect causes the demand for watches to be more than would otherwise be the case (without network externalities). 10000- 8000- 6000- 4000- 2000- Derab 0+ 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Watches (per month) 80
Consider the market for a particular brand of watch, illustrated in the figure to the right. Suppose there are network externalities in this market such that the quantity of the good demanded falls in response to the growth of purchases by other individuals (as indicated by the demand curve "Demand" in the figure). Suppose that the price is initially $14,000 where the quantity demanded is 60 watches per month. 18000- 16000- 14000- E3 12000- If the price of this brand of watch falls to $10,000, demand will increase to watches. (Enter your response using an integer.) However, without negative network externalities, demand would have increased by ☐ units, which is the pure price effect, meaning the size of the snob effect is (Enter your responses using integers.) The snob effect causes the demand for watches to be more than would otherwise be the case (without network externalities). 10000- 8000- 6000- 4000- 2000- Derab 0+ 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Watches (per month) 80
Oh no! Our experts couldn't answer your question.
Don't worry! We won't leave you hanging. Plus, we're giving you back one question for the inconvenience.
Submit your question and receive a step-by-step explanation from our experts in as fast as 30 minutes.
You have no more questions left.
Message from our expert:
Our experts need more information to provide you with a solution. Provide clear graph for the question. Please resubmit your question, making sure it's detailed and complete. We've credited a question to your account.
Your Question:
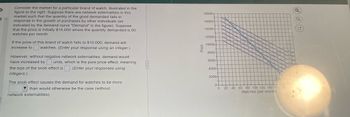
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the market for a particular brand of watch, illustrated in the
figure to the right. Suppose there are network externalities in this
market such that the quantity of the good demanded falls in
response to the growth of purchases by other individuals (as
indicated by the demand curve "Demand" in the figure). Suppose
that the price is initially $14,000 where the quantity demanded is 60
watches per month.
18000-
16000-
14000-
E3
12000-
If the price of this brand of watch falls to $10,000, demand will
increase to watches. (Enter your response using an integer.)
However, without negative network externalities, demand would
have increased by ☐ units, which is the pure price effect, meaning
the size of the snob effect is (Enter your responses using
integers.)
The snob effect causes the demand for watches to be more
than would otherwise be the case (without
network externalities).
10000-
8000-
6000-
4000-
2000-
Derab
0+
0
20
40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Watches (per month)
80
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you









Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax
