Calculating dG from dH and dS chemical engineer is studying the two reactions shown in the table below. In each case, she fills a reaction vessel with some mixture of the reactants and products at a constant temperature of 134.0 °C and constant total pressure. Then, she measures the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS of the first reaction, and the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction free energy AG of the second reaction. The results of her measurements are shown in the table. Complete the table. That is, calculate AG for the first reaction and AS for the second. (Round your answer to zero decimal places.) Then, decide whether, under the conditions the engineer has set up, the reaction is spontaneous, the reverse reaction is spontaneous, or neither forward nor reverse reaction is spontaneous because the system is at equilibrium. 2NOCI(g) 2NO(g) + C₁₂ (g) →>> 2NH3(g) →>> N₂H₁ (g) + H2(g) AH = 76. kJ J AS = 107. K ☑ AG = KJ Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neither AH 188. kJ J AS = K AG 31. kJ Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neither ? 000 18 Ar
Calculating dG from dH and dS chemical engineer is studying the two reactions shown in the table below. In each case, she fills a reaction vessel with some mixture of the reactants and products at a constant temperature of 134.0 °C and constant total pressure. Then, she measures the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS of the first reaction, and the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction free energy AG of the second reaction. The results of her measurements are shown in the table. Complete the table. That is, calculate AG for the first reaction and AS for the second. (Round your answer to zero decimal places.) Then, decide whether, under the conditions the engineer has set up, the reaction is spontaneous, the reverse reaction is spontaneous, or neither forward nor reverse reaction is spontaneous because the system is at equilibrium. 2NOCI(g) 2NO(g) + C₁₂ (g) →>> 2NH3(g) →>> N₂H₁ (g) + H2(g) AH = 76. kJ J AS = 107. K ☑ AG = KJ Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neither AH 188. kJ J AS = K AG 31. kJ Which is spontaneous? this reaction the reverse reaction neither ? 000 18 Ar
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter13: Spontaneous Processes And Thermodynamic Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 39P
Related questions
Question
100%
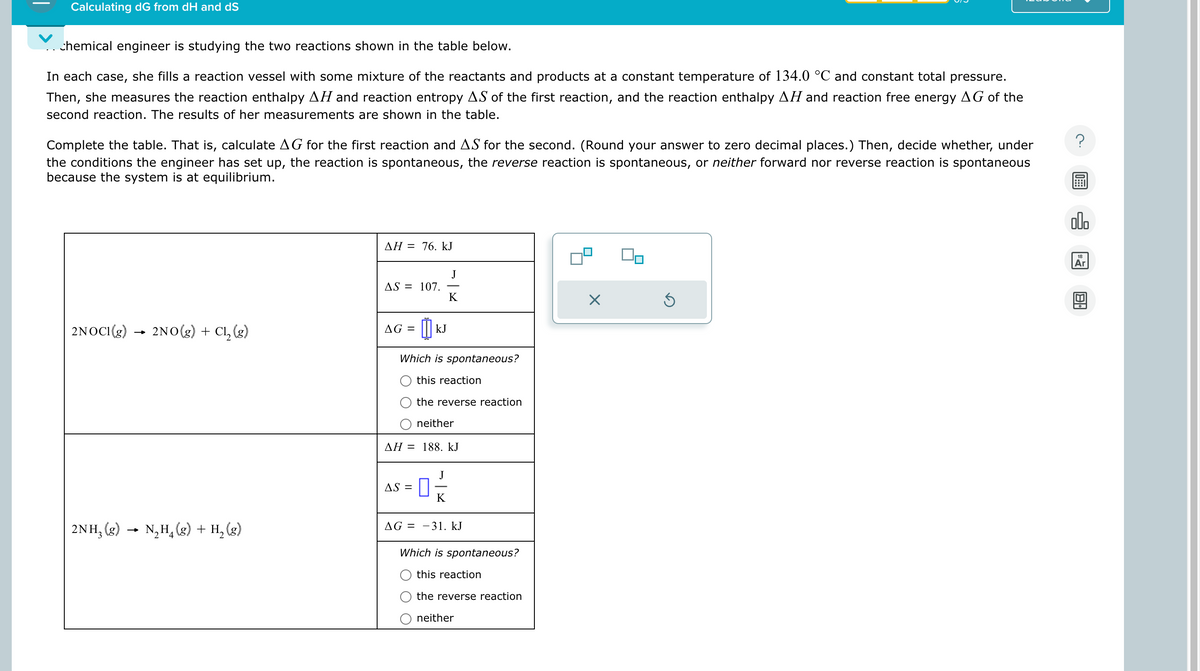
Transcribed Image Text:Calculating dG from dH and dS
chemical engineer is studying the two reactions shown in the table below.
In each case, she fills a reaction vessel with some mixture of the reactants and products at a constant temperature of 134.0 °C and constant total pressure.
Then, she measures the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS of the first reaction, and the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction free energy AG of the
second reaction. The results of her measurements are shown in the table.
Complete the table. That is, calculate AG for the first reaction and AS for the second. (Round your answer to zero decimal places.) Then, decide whether, under
the conditions the engineer has set up, the reaction is spontaneous, the reverse reaction is spontaneous, or neither forward nor reverse reaction is spontaneous
because the system is at equilibrium.
2NOCI(g) 2NO(g) + C₁₂ (g)
→>>
2NH3(g)
→>>
N₂H₁ (g) + H2(g)
AH = 76. kJ
J
AS = 107.
K
☑
AG = KJ
Which is spontaneous?
this reaction
the reverse reaction
neither
AH 188. kJ
J
AS =
K
AG 31. kJ
Which is spontaneous?
this reaction
the reverse reaction
neither
?
000
18
Ar
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133958437
Author:
Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:
Wadsworth Cengage Learning,